about the present and prospects of healthcare
In the medical field, AI emergency care is seen as vital. The gap between the latest technological achievements and real medical practice, which is far from ideal, not just in one country, but throughout the world, turned out to be too large. In an interview The New York Times Bhavik Patel, MD, MBA, Mayo Clinic, Arizona, opined:
There are many gaps in healthcare today, and I think we can intelligently use artificial intelligence to close them, or at least minimize them.
Let's look at how AI can help in medicine and what steps are being taken in different countries.
Moscow diagnostic practice
A huge amount of data accompanies the treatment of each patient. This is not a problem for AI, which is why the technology is being actively implemented around the world. For example, from the summer of 2023 in capital clinics testing AI service, which helps doctors identify ischemic stroke. Diagnostic tool developed in the SberMedII laboratoryallows you to timely identify the disease and carry out therapeutic measures that save lives.
It is not by chance that ischemic stroke was chosen for the implementation of the technology – here the doctor literally enters a race against time. Dissolving a small blood clot should take a maximum of 4.5 hours, removing a large blood clot should take no more than 6 hours. The program has already demonstrated diagnostic accuracy of 93%, opening up wide opportunities for using the service in medical practice.

Thanks to AI-based systems, doctors can cope not only with ischemic stroke, but also with other dangerous conditions, for example, oncology, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes.
Robots against cancer
In the field of diagnosis and treatment of oncology, artificial intelligence is used at all stages of patient management. As in the case of cardiovascular diseases, here we are talking about the life and death of the patient.
Today, there are over 100 types of cancer. Every fifth person on the planet develops some kind of phenotype. Mortality rate remains high: 1 in 9 affected men and 1 in 12 women die from cancer. Statistics show steady growth identified cases. And although the increase is associated with improved diagnosis, it is impossible to rely only on old methods of recognizing the disease – they are ineffective.
In oncology, the cost of error is especially high. If the diagnosis is made correctly at an early stage, the patient is likely to recover close to 90–98% (depending on the type of disease). Lost time quickly reduces the chances to zero. The main difficulty is not to see the cancer itself, but to recognize its phenotype.
Smart systems reduce the number of false positive conclusions, provide clear localization of the tumor, and increase the accuracy of diagnosis by 30–40% – this is on average, there are even more impressive results. For example, according to the diagnosis of breast cancer AI accuracy was 61.8% higher compared to radiologists. In addition, using neural networks research time is reduced from hours to several minutes.
Help from AI makes cancer research personalized and therefore more successful. The doctor receives not only information about the diagnosis, but also about the prognosis of treatment and the response to the prescribed therapy. In the near future, scientists and practitioners plan to transfer oncology diagnostics to a fully automatic mode.
Robotic shuttles for drug delivery
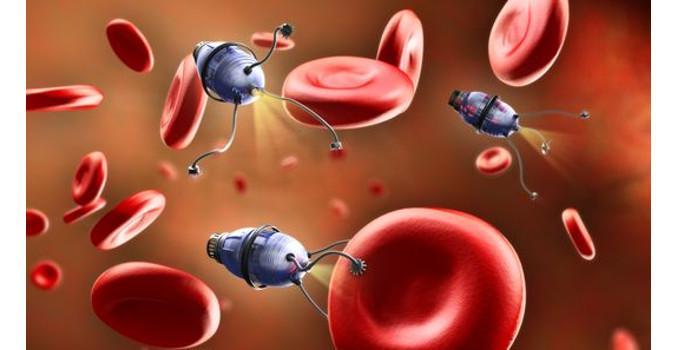
Therapy is another area where AI is expected to provide significant help. The fact is that oncological drugs create a huge burden on the body, since they are delivered not targeted, but fan-out, that is, to both sick and healthy organs. Shuttle robots capable of transporting the drug in a dosed manner and precisely to the tumor. The “shuttle” with a cavity for the drug is controlled by a magnet. When approaching the affected area, the acidity of the environment changes, a “door” opens in the delivery device and the useful substance goes directly to the site of the pathology.
An experiment on mice showed that only one dose of medicine delivered by a nanorobot reduces tumor by 90%. To achieve a comparable result with a traditional course, it will take from 6 to 14 procedures, so the potential of robotic shuttles is enormous.
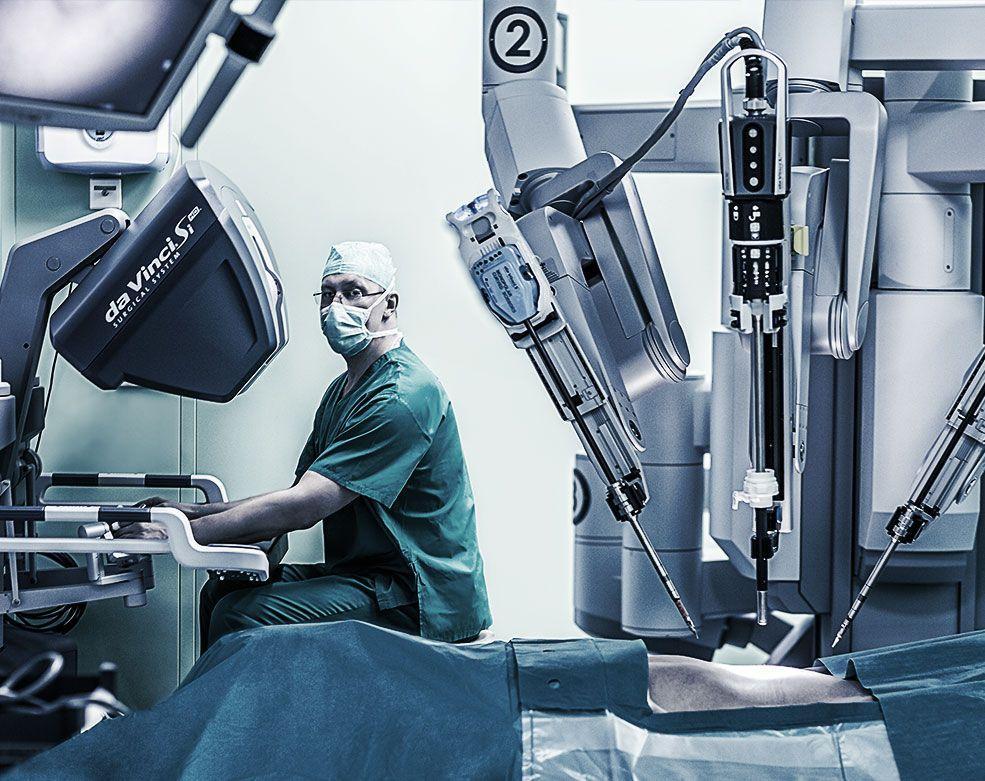
robot surgeon Da Vinci
Treatment for cancer involves surgery, which is also hard on a body already fighting cancer. New technologies can significantly reduce the harm from an invasive procedure by Da Vinci manipulator. The device has two blocks. One is controlled by a surgeon, the second by a robot with four “arms”. A person transmits commands to his “subordinate”, who performs quick and accurate manipulations. As a result of teamwork, it is possible to carry out many hours of operations without fatigue, erroneous actions or loss of concentration.
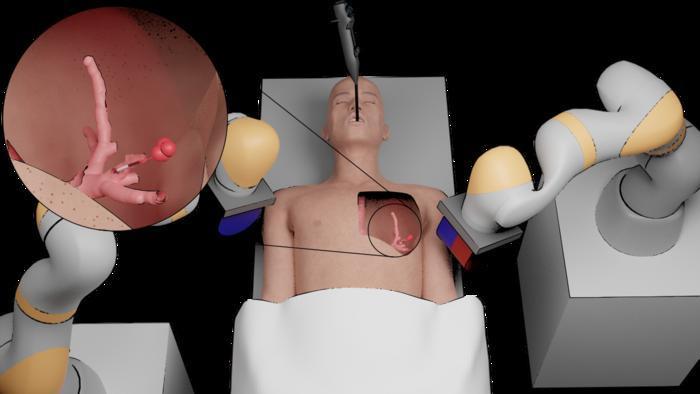
Tentacle robot for lung research
Another diagnostic tool was created to examine areas and organs of the body that are inaccessible to humans. Compared with standard equipment, the thin elastic tentacle can not only penetrate further and deeper by 37%, but also give a clearer and more accurate picture. The revolutionary instrument is already being used to take biopsy samples and carry out targeted non-invasive treatment of tumors, which does not affect healthy organs and tissues.
What is personalized treatment
The success of artificial intelligence in the medical field has changed attitudes towards technology. Today she is no longer perceived as an assistant, but as a full participant in the process of diagnosing and treating patients.
How to use smart programs:
In surgery. Robotic mechanisms are used to carry out complex operations, and this is not the only area of application of intelligent tools. AI helps by collecting information and analyzing incoming data in real time. As a result, right during an invasive intervention, the surgeon has the opportunity to correctly assess the situation and make an informed decision.
Gene therapy. Based on the collected data, personalized treatment plans are developed, selecting medications and therapeutic regimens depending on the individual patient.
Prescription of drugs. Here, individual intolerance to drugs is taken into account, and the positive effect of therapy on the patient’s condition is assessed.
In training young doctors. AR and VR technologies, integrated with AI, are used as virtual simulators for young specialists to practice skills and gain practical experience.
It is obvious that the scope and depth of AI implementation in various areas of medicine will only grow. In addition to surgery and therapy, smart systems will accelerate the development of new medicines, reduce the time and financial costs of research, and expand access to medical care in regions with difficult access.
Physicians and policymakers expect that in the near future, the less effective reactive system of care that exists today will give way to a fast and precise preventative model of health care, where it will be possible to prevent diseases before they have a chance to cause harm. There is a large dependence on the effectiveness of AI on the accuracy of the input data. Their incorrectness can lead to dangerous conclusions.
Chatbot in the fight against bureaucracy
Currently, the structure of work in the medical field is largely based on management models of the last century. Doctors and junior medical staff are still immersed in paperwork. This takes away the time needed to examine patients, and yet a way out of the situation has already been found.
Using ChatGPT manages to generate completely readable texts based on basic data on diagnoses and previously prescribed therapy. Thus, the robot helps reduce the time required to compile mandatory correspondence—it takes about a minute to write one letter. Another DocsGPT system is used for drawing up documents, referrals, appeals, post-operative appointments, etc.
Robots were given access to extensive libraries of templates and other information accumulated in medical practice over decades. And if a person is not able to extract useful information from there due to limited speed, then for a chatbot there is no such problem. As a result, routine is gradually disappearing from medical practice. Both doctors and patients benefit.
About the benefits of visualizations
Three-dimensional computer graphics allows you to recreate any part of the body with extreme realism. This helps in diagnosis, therapeutic and surgical plans, training of young specialists.
Reconstructions are prepared on the basis of ultrasound scanning, CT, MRI, supplementing the visualized image with tactile technologies. Scenarios are practically no different from states real patients. This increases the accuracy of upcoming manipulations on living people, while simultaneously reducing the traumatic nature of interventions.
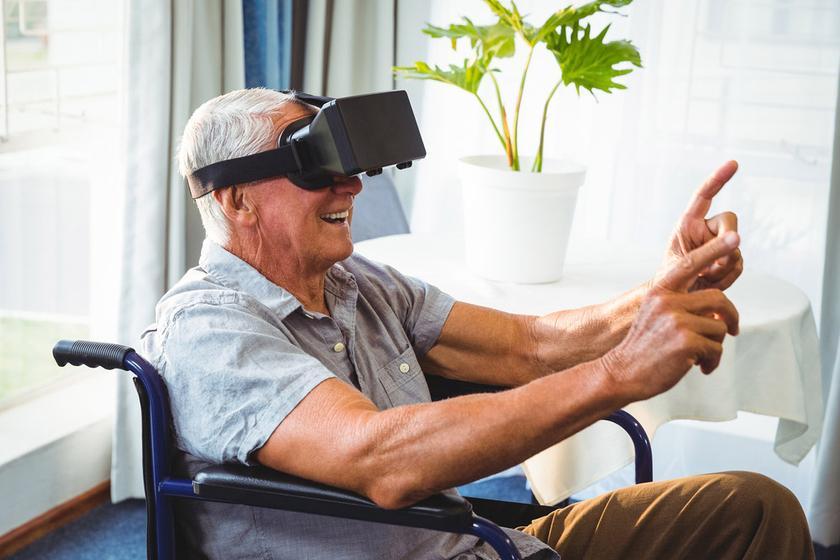
Who does VR glasses help?
Today, with the help of virtual reality, you can simulate any medical situation from planning complex surgeries to treating patients with phobias and severe pain. Just one tool – smart glasses – is used to train young specialists, in telemedicine to make a diagnosis, for vision correction for diabetes and age-related changes, for the recovery of patients with mental disorders.
In the gerontological center of Russia VR glasses used for the rehabilitation of age-related patients, including those with strokes and fractures. A patient wearing glasses does not need to overcome apathy and perform mechanical movements. Everything is much simpler and more interesting. For example, motor activity of the upper limbs is restored with the help of “stroking” and “feeding” dolphins. The legs are developed through tasks involving raising the feet while a virtual stingray “swims” under them. Movements are practiced without the risk of injury, without routine and mental effort. The fun process increases confidence and develops skills, helping older patients return to normal life faster.

Should you trust a virtual doctor?
An AI assistant is an absolute plus of our time, but how far can the help of an even smart, but still inanimate system go?
In November 2023 Forward Health company presented a medical office completely controlled by artificial intelligence. The CarePod station is designed for installation in shopping centers and office buildings especially for those who do not like to visit hospitals.
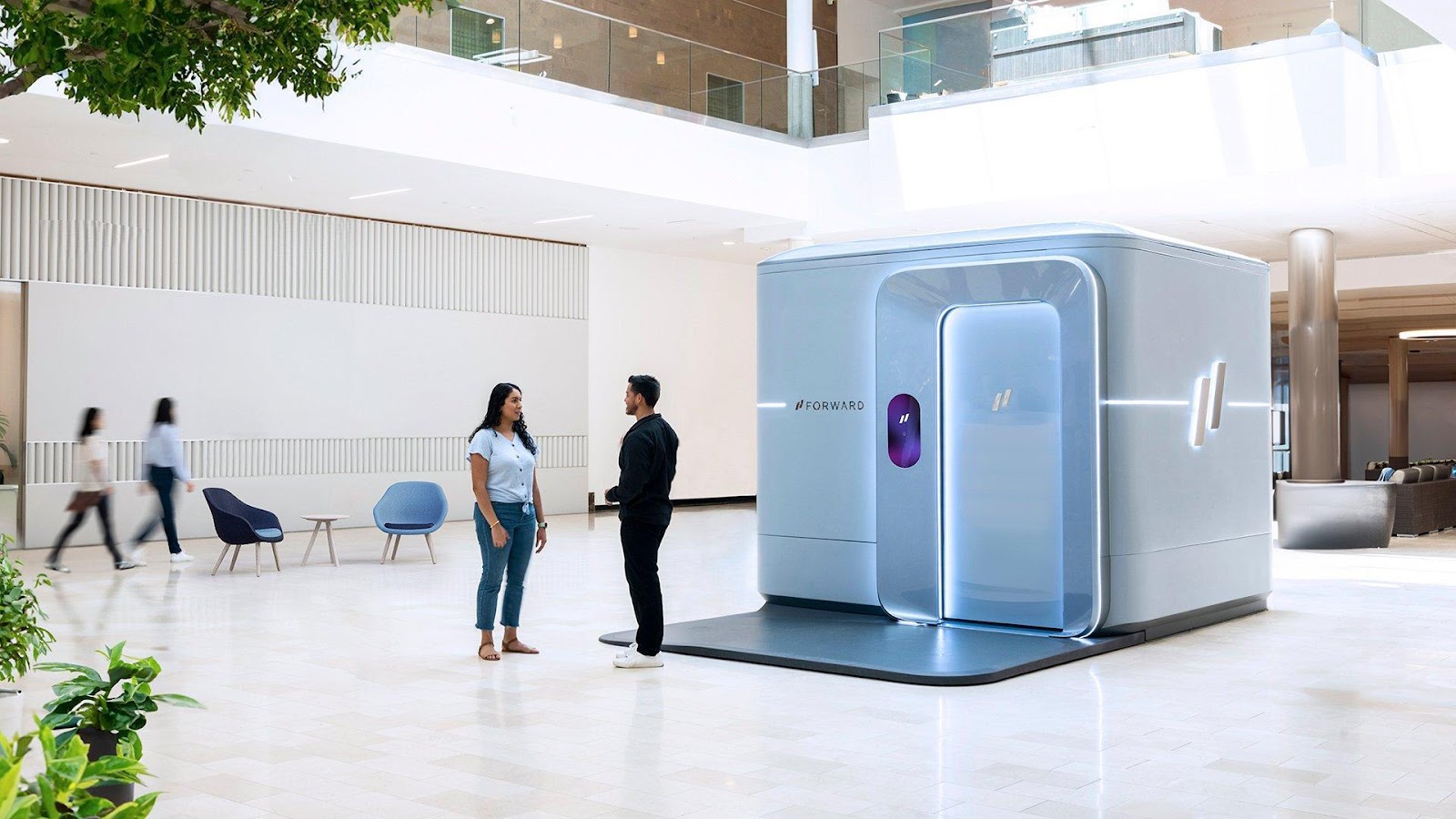

The client who issued service subscription, can come inside and undergo scheduled examinations, such as checking blood pressure, mental status, heart function or performing a body scan. The entire process takes place one-on-one with the smart box – no personnel are provided inside. However, if in doubt, you can contact your doctor using the mobile application.
Running tests is just one way to use AI. The main direction for introducing technology remains the analysis of incoming data.
Today, a gigantic amount of information collected about patients lies unclaimed – there is simply no one to analyze it. During 3 months of storage, doctors have time to review less than 15% of data. With the help of AI, you can streamline routine and make archival materials useful by correctly setting search algorithms.
However, extreme caution must be exercised in this matter and not rely solely on artificial intelligence. The performance of services should not be taken as an absolute guarantee of the accuracy of state determination. AI does not diagnose, but compares the studied parameters with samples, and this is its key difference from a human doctor.
Estimated McKinsey, the average potential for healthcare automation is about 36%. In the work of junior medical personnel, this figure drops to 30%, and for dentists to 13%. And even this share cannot be completely transferred to the control of artificial intelligence, since it has not yet been possible to cope with the shortcomings of virtual assistants, but they exist.
The attitude of the general public towards the idea of introducing AI into medicine is also ambiguous. By according to VTsIOMif a doctor relies on artificial intelligence to diagnose diseases and recommend treatment, then this will be unpleasant for 49% of Russians and 60% of Americans, while 40% and 39% of respondents, respectively, would be calm about this.
Risks of AI implementation
Confidentiality of stored information. As intelligent systems gain access to proprietary medical data, it is necessary to develop mechanisms to protect patients.
Errors in diagnosis. AI is still not perfect, so the final decision in making a diagnosis, prescribing therapy and surgical intervention must remain with the person.
Dependence of the estimate on the conditions of the introduced problem. If the AI receives incorrect input, it will produce an erroneous conclusion. It is important to improve the data collection processes required to set the task. The result must be controlled by a person.
Safety. The introduction of AI could create channels for attacks on healthcare companies. By statistics from Forrester Consulting, 88% of people responsible for making security decisions do not exclude this possibility. The new threat can be countered by AI-based defense systems.
In addition, the issue of integrating smart technologies with existing medical processes has not yet been resolved. Now responsibility for making decisions and progressing treatment lies entirely with doctors. The future will show how the situation will change.
conclusions
We are still very far from the time when AI will be able to independently diagnose and treat people. However, technologies are already providing invaluable assistance to patients with cardiovascular diseases, oncology, diabetes and other dangerous diseases. In order for systems to become an integral part of medical practice, developers must minimize the risks of using intelligent tools, and legislators must define areas of responsibility in the event of an error.