Root certificate stores in browsers. The main trusted centers of the Internet

In December 2022 from the Mozilla root repository expelled TrustCor root certificates (more precisely, they are labeled Distrust for X After Date from 01.12.2022). The reason was cooperation with companieswho have ties to the US intelligence community. To this Mozilla decision later have joined Apple, Google and Microsoft. Thus, the certificates of a large CA instantly depreciated on most user devices.
Moreover, “trust in TrustCor” added to the global database of vulnerabilities. Now if you host code on GitHub that trusts TrustCor certificates, the system reports a moderate vulnerability.
Root certificate stores
Root stores are the underlying stores of trusted root CAs. For example, Microsoft storage used to verify certificates in the Windows operating system, and Mozilla repository used to verify certificates by Chrome, Firefox browsers, as well as the Linux operating system.
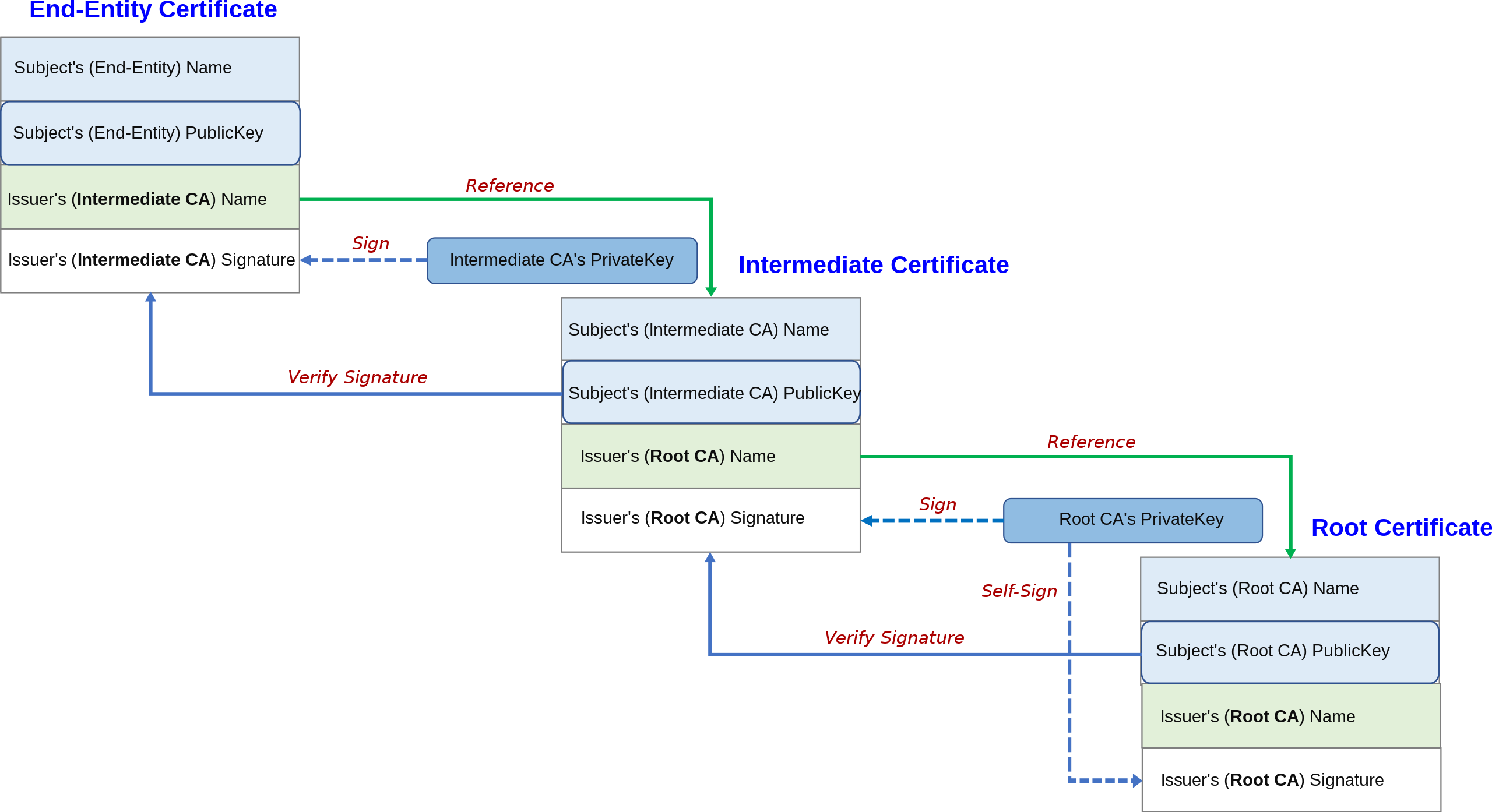
The Role of Root Certificates in the Chain of Trust
Apple has its own root store, but it uses certificates from other root certificate sets such as the Mozilla Root Store to verify the chain of trust.
History of TrustCor
TrustCor Systems – a Panamanian CA that has been criticized by the entire industry after investigations Washington Post. As it turned out, this CA actively cooperated with spyware developers and other companies that have close ties to the US intelligence community. They issued TLS certificates, including by Packet Forensics (Measurement Systems) mobile applications, which were seen in spying on android users.
Representatives of TrustCor tried to justifybut their fate was sealed.

There is a public mailing list dev-security-policy@mozilla.org, the major browser vendors decide whether they should continue to trust a particular CA. Sometimes representatives of this CA take a hostile position in the style of “What are you going to do, remove us from the repository?”, And in some cases, the developers actually do it. As happened in this case. And that could spell the end for the company, because it’s hard to sell certificates that web browsers don’t trust.
TrustCor discussion became a record thread in the history of the mailing list dev-security-policy@mozilla.org And was closed after 12,239 pages of heated debate.
Why some state CAs will not get into browsers
As can be seen from the previous story, the developers are closely monitoring that dubious CAs that are seen in relations with government agencies do not get into the trusted storages. At the same time, the government agencies themselves of different countries often try to penetrate the Internet’s global trust system, and if this fails, they create an alternative trust system.
At least since 2016, the Ministry of Digital Development of the Russian Federation started working on the creation of a Russian head certification center for issuing SSL certificates. In 2017, testing of this CA began, and a few years later, the issuance of certificates began.
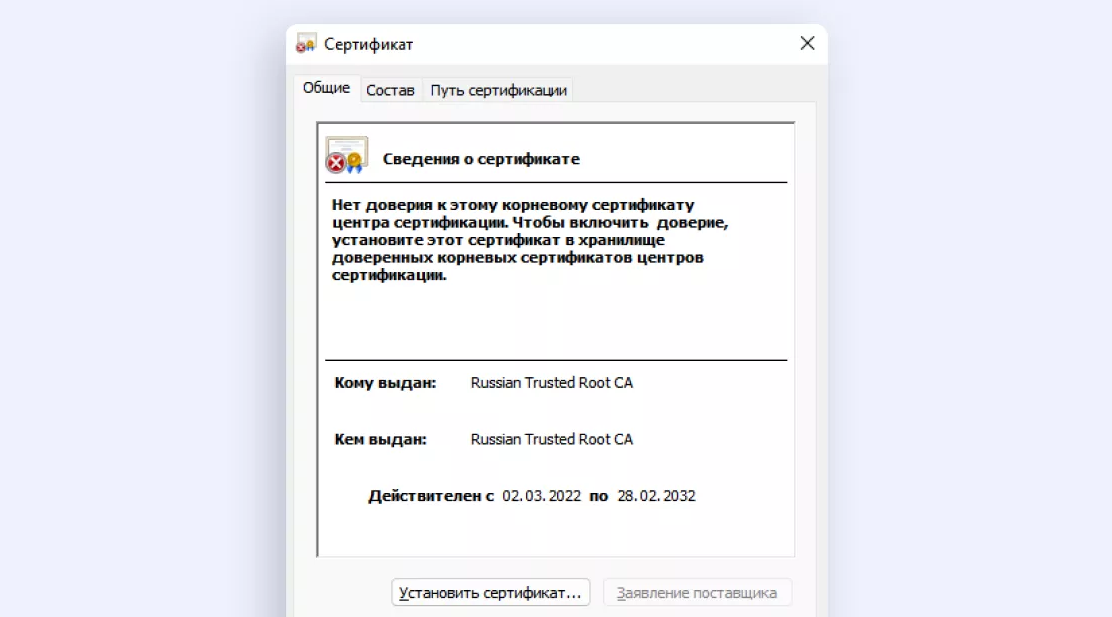
In 2022, plans were announced in response to the revocation of foreign TLS certificates issue free domestic certificates for organizations. Although certificate revocations from Russian sites were limited to individual CAs and the problem gradually disappeared, Sberbank and several other companies still switched to Russian TLS certificates. As of April 2023, this has been done 4883 sites (the same number was in September 2022, screenshot). That is, the process has not acquired a mass character. The websites of Gosuslug, the Central Bank and other government agencies remained on standard certificates included in the global Internet trust system:

Information security experts have a negative attitude to include government certificates in root stores. In their opinion, such certificates do not deserve much trust. And it’s not about any particular country, but about the introduction of any state bodies (of any country) into the global system of trust.
Therefore, it seems extremely unlikely that Russian Trusted Root CA to the Mozilla and Microsoft root stores. Access to these sites via HTTPS will only be possible from Russian browsers (for example, Yandex Browser) or if the user independently install root certificate for your device. But in this case, these Russian sites will be partially isolated from the global system of trust, with all the ensuing consequences for their availability and security.