Digest of sci-fi news for the week, about which we did not write anything
and / or write an article in the “Sandbox” and send me a link.
And today I will again go over the news of the outgoing week, which our editorial staff should have covered in more detail, but it did not work out, because we are not multi-armed.
Astronomers have found a hot Neptune that should not exist
At a distance of 1800 light-years from us, an unlikely rare planet orbits an old star. This type of planet is called a “hot Neptune” and is one of a small number of hot Neptunes discovered by astronomers. Hot Neptunes are so close to their stars that powerful stellar radiation should have destroyed their atmospheres, leaving only the planetary core. But this planet somehow retained its atmosphere.
This hot Neptune is so close to its star that it completes its entire orbit in just 4.2 days. The planet, named TIC 365102760 b, is not very dense. Although its radius is about half that of Jupiter, its density is only 0.06 that of Jupiter. At such a low density, the planet shouldn’t have the strength to hold on to its atmosphere.
This planet is the rarest of the rare. There are only a handful of Neptune-sized planets orbiting a main sequence star, and this is the only hot Neptune orbiting a star of this type. Such uncharacteristic celestial bodies are interesting because they show us the limits of nature and help scientists build better models.
Existing models cannot explain TIC 365102760 b and show that nothing but the core should be left of it. “Thus, assuming that the planet did not experience migration or inflation after the system reached the age of 20 million years, then most or all of the planet’s atmosphere should have been destroyed during its existence,” authors write.
An anatomy expert explains why sitting cross-legged is bad

Pay attention to your posture. What are your feet doing? Are they crossed? What leg do you have on top? About 62% of people put their right foot over their left, 26% do the opposite, and 12% have no preference.
There are usually two ways to sit in a chair and cross your legs: one is with your foot on your knee, the other is on your ankle. But as comfortable as it is to sit cross-legged, studies show that such a position is unhealthy and unhealthy for posture.
Research shows that sitting cross-legged can cause the hips to shift when one hip is higher than the other. It also changes the speed at which blood moves through the blood vessels in the lower extremities, which can increase the risk of blood clots.
Most studies show that crossing your legs, putting your foot on the knee of the other, is worse than putting your foot on the ankle. This posture can lead to an increase in blood pressure due to the accumulation of blood in the veins, and the heart has to overcome this obstacle. This can increase the risk of damage to blood vessels, so make sure your feet are flat on the floor when your blood pressure is taken.
If possible, it is better not to cross your legs. However, many of the risk factors associated with crossing your legs are likely exacerbated by other underlying problems such as sedentary lifestyles and obesity. Therefore, the main advice is not to sit too long in one position and regularly lead an active lifestyle.
AI helped prove that many second-generation stars were enriched with elements born in supernovae
The first stars, born shortly after the Big Bang, were mostly hydrogen and helium. The next generation of stars contained only a small amount of the heavy elements produced by the first stars. To understand the evolution of the universe, researchers need to study these stars, which are poor in “metals,” as astronomers call all elements heavier than helium.
Fortunately, these second-generation metal-poor stars are observed in our Milky Way Galaxy. Based on a newly developed supervised machine learning algorithm trained on theoretical models of supernova nucleosynthesis, they found that 68% of observed extremely metal-poor stars have a chemical signature that suggests they were enriched with elements from several previous supernovae.
“Our result suggests that most early stars formed in small clusters, so many of their supernovae could contribute to the metal enrichment of the early interstellar medium,” said lead author Hartwig.
“The theory of the first stars tells us that they must have been more massive than the Sun. It was natural to expect that the first star was born in a gas cloud with a mass a million times greater than that of the Sun. However, our new find suggests that the first stars were not born alone, but were formed as part of a star cluster, a binary or multiple star system. This also means that we can expect the presence of gravitational waves generated by the first binary stars that can detect future missions in space or on the Moon, ”said one of the authors of the work, Professor Chiaki Kobayashi.
Scientists have identified six problems that a person will have to deal with when implementing AI
Lead researcher Ozlem Gharibay, assistant professor of industrial engineering and control systems at UCF, says technology has become more prominent in many aspects of our lives, giving rise to many issues that need to be carefully examined.
For example, the coming ubiquitous integration of artificial intelligence could significantly impact human life in ways that are not yet fully understood, says Garibai, who works on the use of AI in the development and discovery of materials and medicines, and how AI affects social systems.
Garibay and a group of researchers determined six important challenges that need to be addressed.
- Human well-being: AI must be able to find opportunities that increase human well-being. It must also be considerate of the well-being of the user interacting with the AI.
- Responsibility: The benefits of AI must be used in a way that is consistent with human values and priorities, and reduces the risk of unintended consequences or ethical violations.
- Privacy: The collection, use and dissemination of data in AI systems must be carefully considered to ensure the protection of people’s privacy and to prevent harmful use against individuals or groups.
- Design: At the heart of AI should be a framework that makes it possible to distinguish between low-risk AI, low-risk AI, high-risk AI, and AI that should not be implemented at all.
- Governance and oversight: There is a need for a governance system that takes into account the entire life cycle of AI, from concept to development and implementation.
- Human-AI Interaction: Ethical and fair relationships between humans and AI systems require that interaction be based on the fundamental principle of respect for human cognition. In particular, humans must retain full control over, and be held accountable for, the behavior and outcomes of AI systems.
The study, which was conducted over a period of 20 months, took into account the opinions of 26 international experts with various backgrounds in the field of AI technologies.
Engineers have developed an artificial skin that is resistant to hostile environments, inspired by the squid
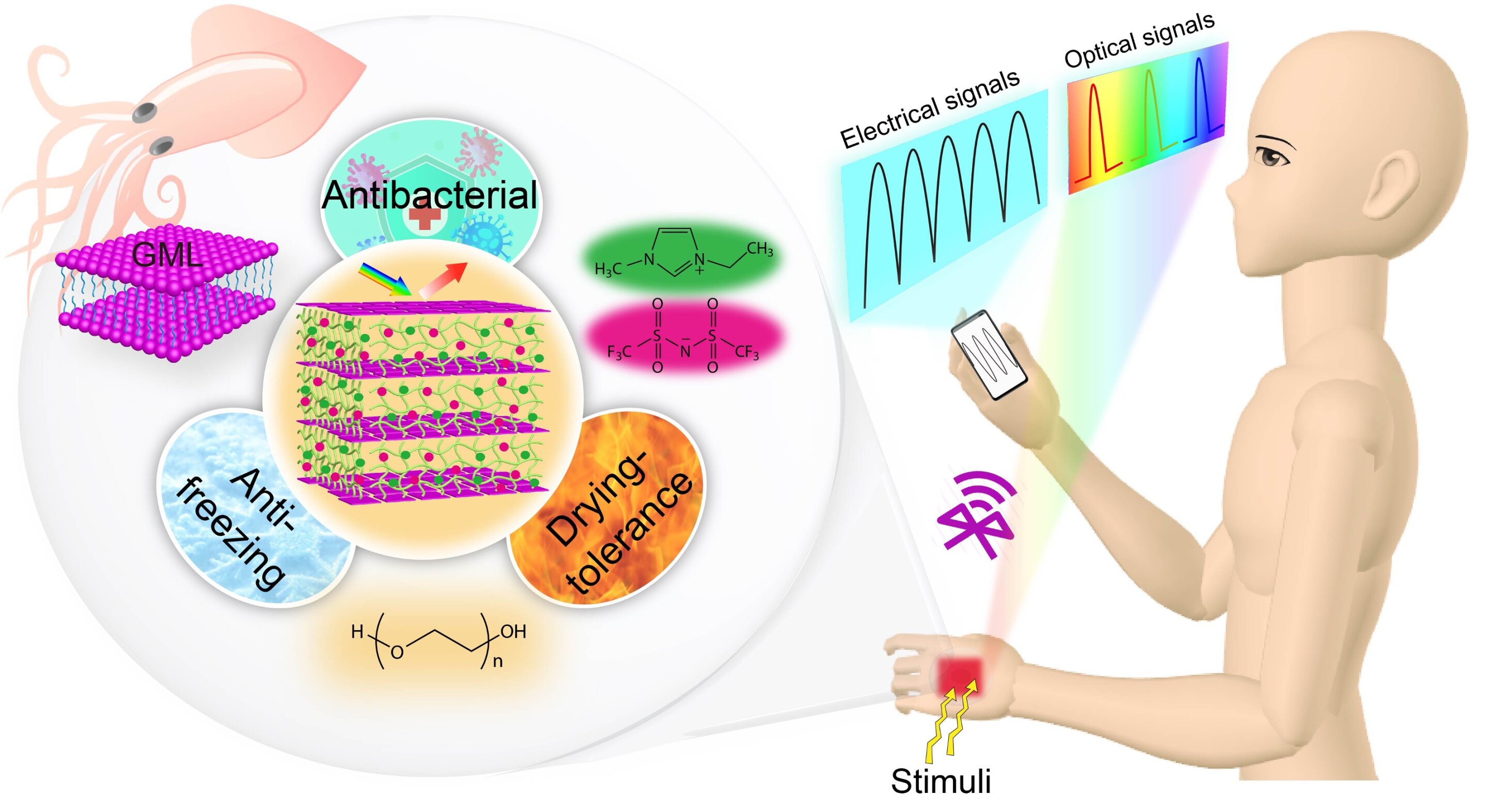
Researchers at Dalian University of Technology in China have created a new artificial skin inspired by the color-changing squid skin. This electronic skin described in the Chemical Engineering Journal, has high flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures, as well as antibacterial properties.
The skin, created by Dr. Niu and his colleagues, is based on a photonic-ion system that allows it to simultaneously emit optical and electrical signals. In addition, monolaurin molecules with antibacterial properties are embedded in it, which allows it to destroy more than 99.9% of bacteria and fungi.
“Squid skin has a bright structural color due to the layered photonic nanoassembly of reflective proteins in iridophores,” explained Dr. Niu. “My colleagues and I successfully created a photonic nanostructure using the hierarchical self-assembly of an antibacterial molecule, monolaurin. This photonic nanostructure was localized in an elastic gel network. Then PEG200 antifreeze and conductive ions were introduced, which made it possible to obtain a photonic ion skin.”