How we tracked down a new APT group that steals passwords and transfers them to Telegram bots

When tracking cyber threats, we, specialists from the Positive Technologies security expert center, once again spotted a previously unknown APT group. Hackers operate in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Armenia, as well as in Central Asia (Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan). According to our data, organizations in the public and financial sectors, education and medicine suffered from their attacks. Total was compromised near 870 employee accounts.
This time we were surprised by the group's handwriting, which can be described as “difficult does not mean better.” Cybervillains are distinguished by the fact that they achieve success without resorting to complex tools, complex tactics and techniques. Their main weapon is a primitive stealer written in Python. The malware reaches the victim using good old phishing and sends the stolen data to telegram bots. As usual, you can view the full report on our blogand below you will find an analysis of the malware and some spoilers.
History of the name, motives and geography of attacks
We called the new hacker group Lazy Koala because of the simple attack techniques, as well as the name of the user who controlled the bots – Koala Joe. “Lazy Koala” is engaged eating eucalyptus espionage and data theft.
In the malicious campaign against the previously mentioned organizations, the number of compromised accounts reached 867, of which 321 were unique.
We have notified all victims and assume that the fate of the stolen data will be resale or use in subsequent attacks on the internal structures of companies.
Although we were unable to determine the exact vector of the attack, indirect signs point to phishing. Cybercriminals skillfully gain the trust of message recipients, convincing them to open the attachment and run the desired file in the browser. The documents we found allow us to evaluate their skill. It is curious that some of them were specifically written in the national language of the victims.




An analysis of the techniques and tools in the attackers’ arsenal, as well as an analysis of the geographic location of the affected companies, did not show any connections with already known APT groups.
Analysis of LazyStealer
Lazy Koala's calling card is a new, previously undescribed stealer of its own design. It is so simple to implement that, by analogy with the group, it was called LazyStealer. The analysis and how it works are described in detail. in the study. In short: the stealer steals logins and passwords from browsers and sends them to telegram bots. Thus, in the attacks we recorded, LazyStealer hunted for credentials that company employees saved in Google Chrome. The choice of messenger for sending is also not accidental: every year Telegram is gaining more and more popularity among criminals.
However, the stealer has fairly good protection, which allows it to evade detection by security tools and slows down the analysis for the researcher. Interestingly, we were unable to discover the LazyStealer's locking mechanism. This may indicate that it is either part of an attack chain or designed to leave no trace. If the latter option is true, then the “lazy koala” attack turns into a one-time attack – this plays into the hands of cybercriminals, since it helps them hide better.
All malware samples we have encountered use PyInstaller as a packer, after which, after removing it in the main script, all code is covered with the Pyarmor protector.
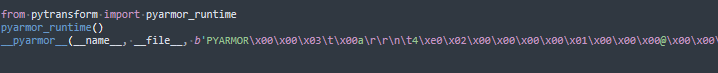
To remove the tread we needed a script bypass.pyinstalled Pyarmor module, as well as the file pytransform.py from this module. This file must be placed in the same folder as the target file with the extension .ру. After removing the tread, we came across a script in one of the sample options. All it does is connect Python modules.
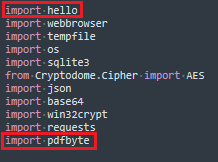
The modules highlighted in the figure, which are named in the file system hello.cp39-win_amd64.pyd And pdfbyte.cp39-win_amd64.pyd, are DLLs built using Cython. They will be launched when they are imported. When compiled via Cython, only string and numeric constants are retained from the original script, and all logic (for example, loops, assignment operations, argument passing) will be implemented natively, so it is not possible to obtain the original script (as is the case with PyInstaller or Pyarmor), but it can be recreated close to the original.
To do this, let's take pdfbyte.cp39-win_amd64.pyd. All logic will happen in a single exported function PyInit_pdfbyte. In this case postfix pdfbyte denotes the name of the module compiled from pdfbyte.pyx. Depending on the name of the module, the postfix of the name of the exported function will also change.
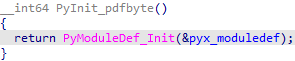
PyInit_pdfbyte
Conclusions and how to protect yourself
As our investigation has shown, Lazy Koala may have companies from different countries and different sectors of the economy in its sights. The hacker group shows that successful attacks do not necessarily require the use of complex utilities, tactics and techniques. All their attacks begin with well-designed phishing messages: employees are tricked into opening a malicious file. To protect against such attacks, on the one hand, specialized tools will be effective, such as a behavioral traffic analysis system (for example, PT Network Attack Discovery) and network sandbox (for example, PT Sandbox). On the other hand, to prevent company employees from falling for hackers, they need to be trained in cyber literacy, regularly test their skills using services for simulating phishing attacks, and also be informed in a timely manner about new fraud schemes.
In our full report A detailed analysis of LazyStealer and its components is provided. We have also highlighted the main Lazy Koala techniques. according to the MITER ATT&CK matrix and indicators of compromise you can use to test your infrastructure.
Vladislav Lunin
Senior Specialist, Information Security Threat Research Department, PT Expert Security Center
More reports PT Expert Security Centerdedicated to new types of malware, the activity of APT groups, techniques and tools of hackers, you can find on the blog.