Youth roadster “Crimea” – new horizons. Part two

The first prototype of the Crimean roadster
What’s the idea?
Let us recall that the idea of the Crimea roadster project is as simple as possible – to make an interesting, and most importantly, affordable car. A team of students worked on the design of the project, noting all the trends and new directions in this industry, and the budget of the car is due to cooperation with AvtoVAZ enterprises. The advantages of a roadster include: the availability of components, low maintenance costs, integration of promising developments and testing them on a given platform, design flexibility and the production itself.
Thanks to the innovative design of the support system and modern technological equipment, it is possible to quickly make changes to the design of the car, which opens up the possibility of using various platforms and power plants, making the roadster a universal platform for scientific research.

Road tests of the second prototype roadster in Crimea
On the basis of the project, various tasks can be solved: an affordable hybrid or electric vehicle, an autonomous vehicle, the development of cyber-protection of a car, development and field testing of promising technical and technological solutions planned for integration into production vehicles and much more.
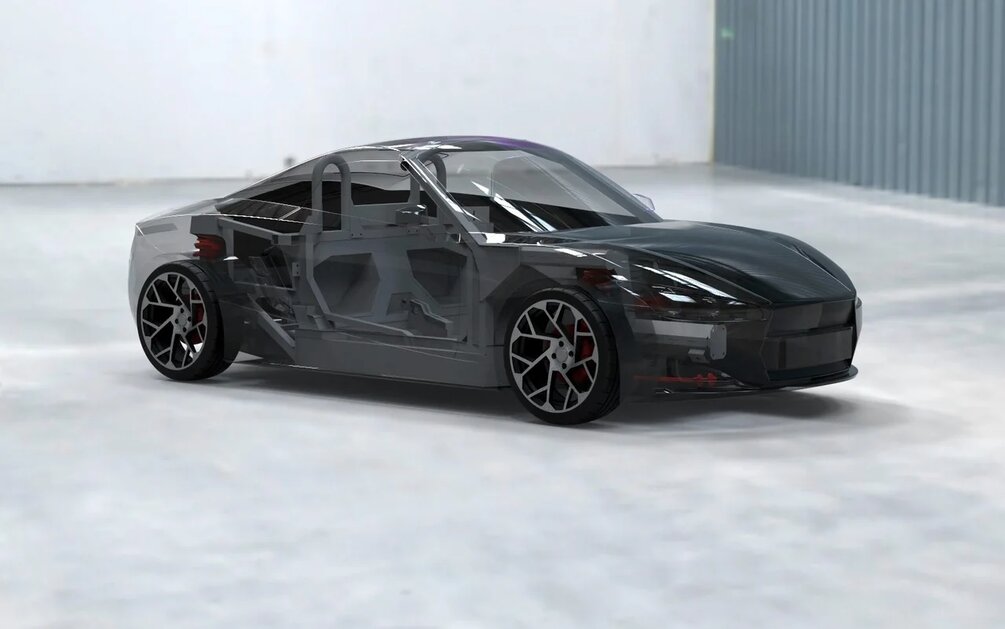
Manufacturability of construction
The manufacturability of the roadster carrier system is dictated primarily by the conditions of future production. The team of young engineers is not a large company with its own dies and machine tools. They are faced with the task of making sure that any average metal processing enterprise can produce all the necessary parts for assembling the frame according to the developed documentation. To create a support system, only three types of operations are required: laser cutting, bending and laser cutting of pipes. The external simplicity of the carrier system is also dictated by the simplicity of production. This, in turn, is a strong argument for scaling the project.
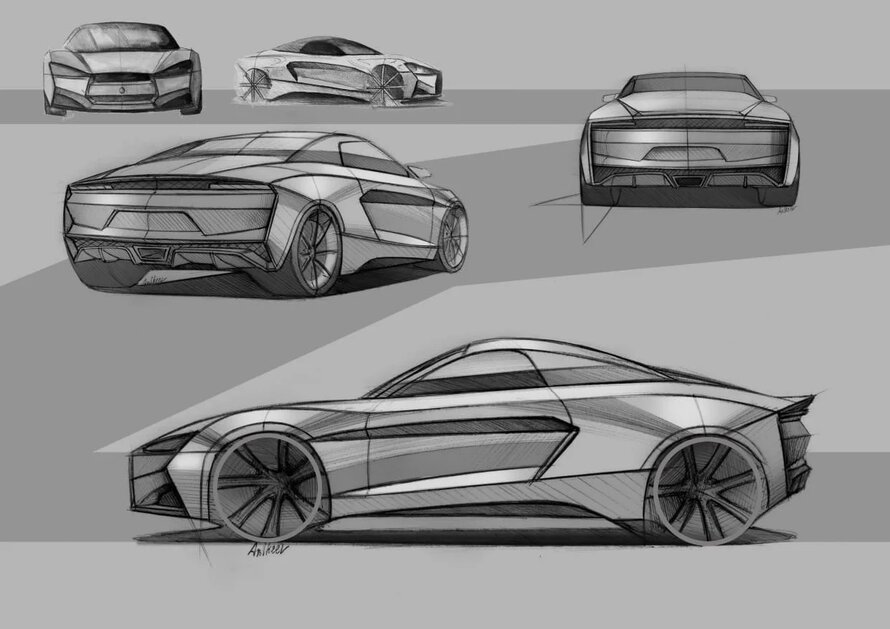

Sketches of the third generation roadster
Despite the apparent simplicity, the calculations took into account all possible loads and vibration effects on flat elements. Where the area is high, a ridge was used. The design itself is technically thought out from the point of view of assembly: each part bases and sets the position of the neighboring one, which eliminates high requirements for the slipway.
There is an inner wall in the threshold, which increases the rigidity and moment of inertia of the section. Frontal and side impact load transfer is also taken into account thanks to virtual crash tests.
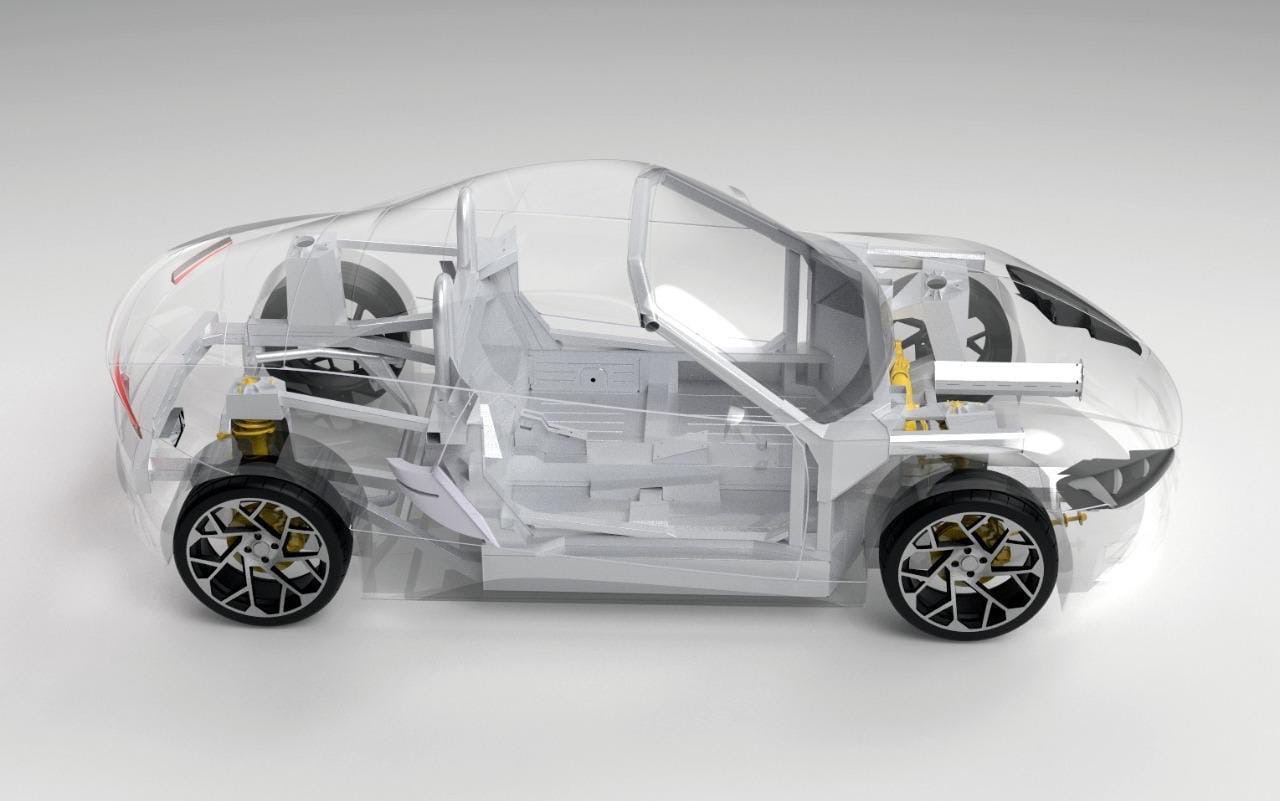

Sectional view of the third generation roadster
Test of strength
The design bureau of the project has been dealing with the issue of passive safety for over a year. When designing the frame, the structure was repeatedly tested in specialized software environments and virtual crash tests were carried out in accordance with the rules of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. To enter the series and receive OTTS, the car must pass real crash tests and check for compliance with standards. At the moment, to create the most efficient energy-absorbing elements, virtual and real tests of the spars have been carried out, which made it possible to verify the mathematical model. As a result, the optimal cross-sectional shape was determined and the material was selected.

3D model of the third prototype roadster
The frame crash tests carried out digitally determined the vector of the iterative development of the structure. For example, tests have been carried out such as a full overlap frontal impact at a speed of 50 km / h according to UNECE regulation 137; impact with 40% overlap at 56 km / h according to UNECE regulation 94; rear impact at 52 km / h according to UNECE regulation 34. In addition, a partial overlap test was carried out in a collision with another vehicle. Based on the obtained picture of the stress-strain state, a decision was made whether it was necessary to revise the designed structure or a specific unit.
Experiments performed
1. Frontal strike with full coverage, rigid barrier. UNECE 137.
Research object mass: 1300 kg.
Speed: 50 km / h.
The front energy-absorbing elements have worked out. Deformation of the side members “accordion” thanks to the programmable deformation zones.
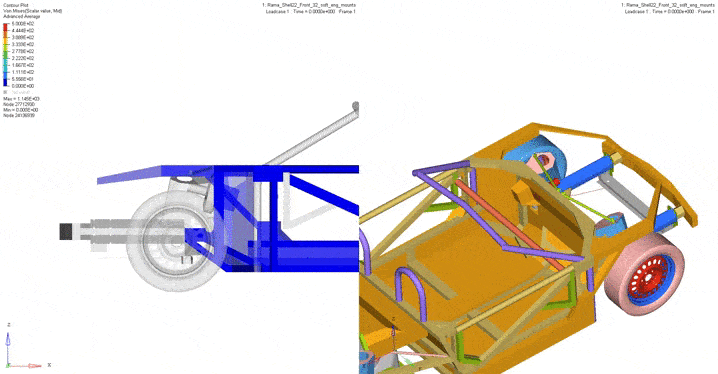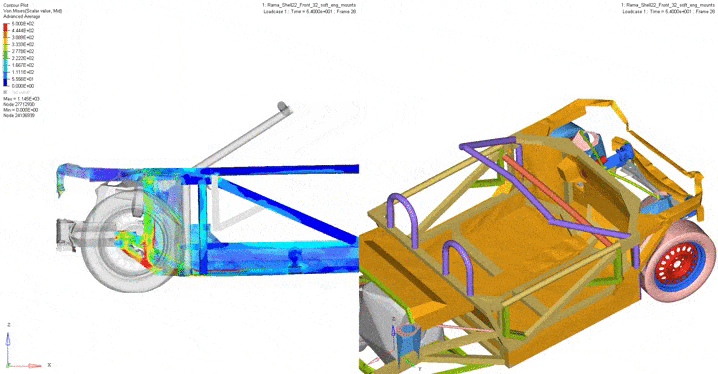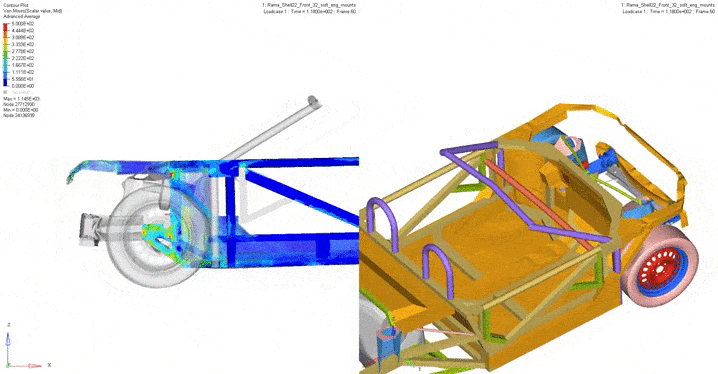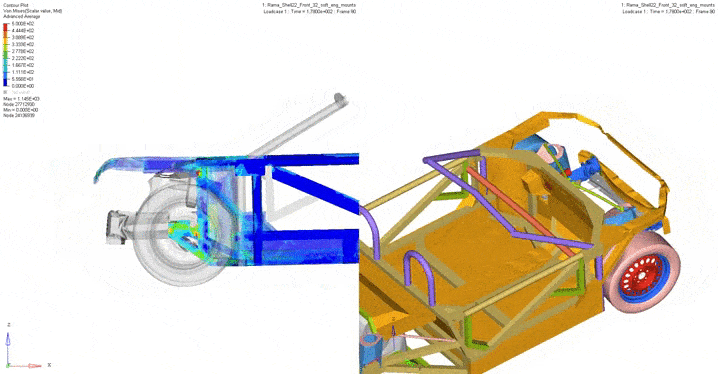
2. Frontal strike with partial (40%) overlap. UNECE 94.
Speed: 56 km / h.
The front energy absorbing elements have worked out. Deformation of spars and cross members at an angle.

3. Impact from behind into a stationary vehicle. UNECE 34.
Speed: 48-52 km / h. The rear energy-absorbing elements have worked. Deformation of the side members “accordion” is similar to the case of a direct impact from the front.

4. Frontal impact with partial overlap with another vehicle.
Car: Ford Taurus, weight 1700 kg.
Vehicle speed: 64 km / h.
Less than in the second car, floor deformations are visible.
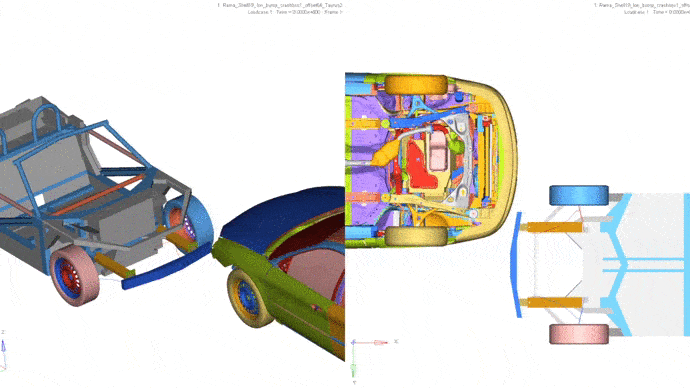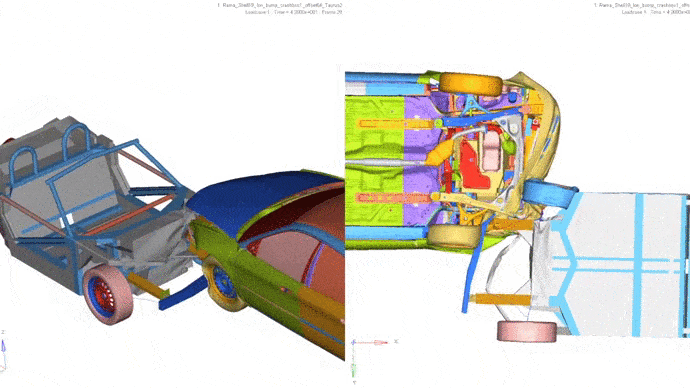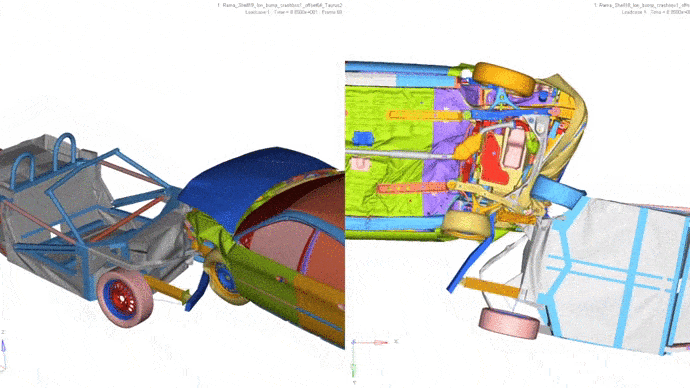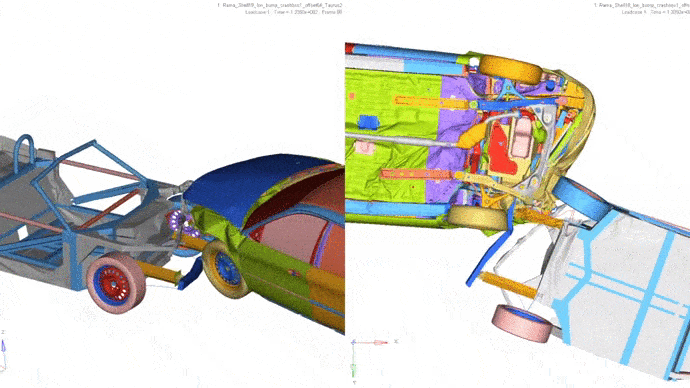
5. Side impact into a stationary vehicle.
Speed: 50 km / h.
The key role is played by the threshold, the door reinforcement, its support (thrust bearing) and the cross tubes that run along the floor of the car and distribute the load on the right side of the frame.

Will there be an electric roadster and an automatic?
An electric roadster is also on the project plans. Several universities of the created Interuniversity Corporation, an association that provides the transfer of knowledge and educational technologies between partner universities, became interested in the design of the electrical version. For example, students from SUSU are planning to build such an electric roadster. The Bauman Design Bureau will build its third ICE prototype. Electric cars will definitely occupy their niche in Russia, but ICE-powered cars will not be replaced for a long time.
Third prototype
The request for an automatic transmission has been repeatedly received from subscribers to the project. The developers are considering the idea of expanding the car’s transmission line. The main planned engine for the basic version of the car is VAZ-21127 or VAZ-21129 with a capacity of 106 hp, which will work in conjunction with a 5-speed manual transmission.
Today there are a lot of options for turbo kits for a standard VAZ engine. Therefore, it is possible to increase engine power in a fairly simple and budgetary way. If this method of forcing is used, the car must be certified immediately with the turbo kit installed on it. Otherwise, the use of a car with a forced engine without registration with the traffic police is illegal.
Currently, the possibility of installing an alternative version of the power plant is being studied – an engine of the EMP family, developed by FSUE NAMI. L4 engine with a volume of 2.2 liters. develops 245 liters. from. and 380 Nm of torque. This unit fits perfectly in the engine compartment of a roadster. The use of the L4 engine will entail an increase in the cost of the car; it can be equipped with more expensive versions of the roadster.
The project team “Roadster Crimea” works in cooperation with the company “KATE”, which is engaged in the design of domestic automatic transmissions. A 9-speed gearbox manufactured by KATE is installed on Aurus vehicles. The roadster is planned to be equipped with a 7-speed automatic transmission FT703. The unit will dock with the AvtoVAZ engine. The main difficulty remains to “make friends” between the power unit and the gearbox: the automatic transmission does not have a torque converter and requires careful tuning for the engine. At the same time, the box has already passed the full range of tests as part of the Lada Kalina car and has proved to be a good side. But for the L4, the torque reserve of the 7-speed automatic transmission is not enough. KBM and NAMI specialists are now working on the most optimal options. Perhaps, for L4 you will have to use a “machine” of foreign origin.
Issue price
The budget is the main component of the project. The planned cost of the basic version of the car is 650-750 thousand rubles. This price is due to two independent marketing studies and is possible if two conditions are met: first – obtaining AvtoVAZ vehicle kits at in-plant prices, second – the serial production must be at least 1000 cars per year. At the initial stage, the cost of cars will be higher, since the first series will be small. In addition, it is planned to sell the car by a kit car, the cost of which will be even less than the cost of the finished car in the basic configuration.

Patented third generation roadster design
The project of Bauman students continues to develop: the guys are studying the possibility of using new technologies, conducting new tests.
In the future, we will continue to share with you the news of the youth roadster “Crimea”. Follow our blog and do not miss new materials




