What is SAP PaPM? (addition)
What is SAP PaPM? (addition)
This is a continuation of the previous article, which discussed the PaPM functions that can generate objects at the SAP HANA database level or at the application server level, in particular, it was about SQL scripts that are used to perform business calculations. At the end of the article, it was concluded that PaPM is good because it is more than just a set of SQL scripts, as it allows you to model, manage calculations, control the progress of execution, and visualize the results of calculations. And this transition from bare SQL to management and modeling was not obvious, I did not show this mechanism for modeling and managing calculations. I am correcting myself.
Standard business content
PaPM comes with standard business content that shows PaPM’s capabilities through simple calculations for various types of businesses:

Let’s take an example for Oil and Gas:

Here are the following features:
Access to data sources. Using data access functions, you can connect to data sources both at the level of SAP BW and SAP S / 4HANA applications (or classic SAP ERP), and at the level of both a local database and remote databases, and almost any ( with appropriate adapters). These features are not specific to PaPM, this is provided by the general functionality of SAP. In this case, SAP BW objects are used. Read more about connections here.
Functions for storing data in tables at the PaPM layer and writing this data to the SAP BW layer (or ERP application layer). You can enter data into the tables of the PaPM environment model manually through the interface or load from a file and then use the write functions to transfer the data to SAP BW objects (ADSO). You can read more about recording functions here.
Using the query functions, you can view data in a customized view structure both within the application itself and using Analysis for Excel. If the query is editable, then you can use the planning function (SAP BW functionality) to edit the key figures either through the application or using Analysis for Excel. You can read more about query functions here.
The calculation functions themselves, which generate SQL scripts when activated.
Query functions with customized filters and custom column and row presentation structure for reporting.
Simulation Flow

A beautiful picture that shows all the elements of the model and their relationships. When diving into a specific function, for example in join “Determining cost center pairs for distribution”, the application shows the relationships in more detail:

Another example:

Process Template
In order for the functions not to remain a set of SQL scripts, but to become part of the process, it is necessary to create a process template with operations in which you need to specify the executable functions and the sequence of their execution:

The process template specifies both the operations to be performed (the actual calculations) and the data input/output operations. By itself, the sequence of functions in the Simulation Environment does not determine the sequence in which calculations are performed, the correct sequence is provided by the process operations.
When defining operations, you can assign commands (groups) Executor And Checker. Users for these groups are defined separately.
Process Instance
To execute the process, a process instance is created, which is then deployed (released):
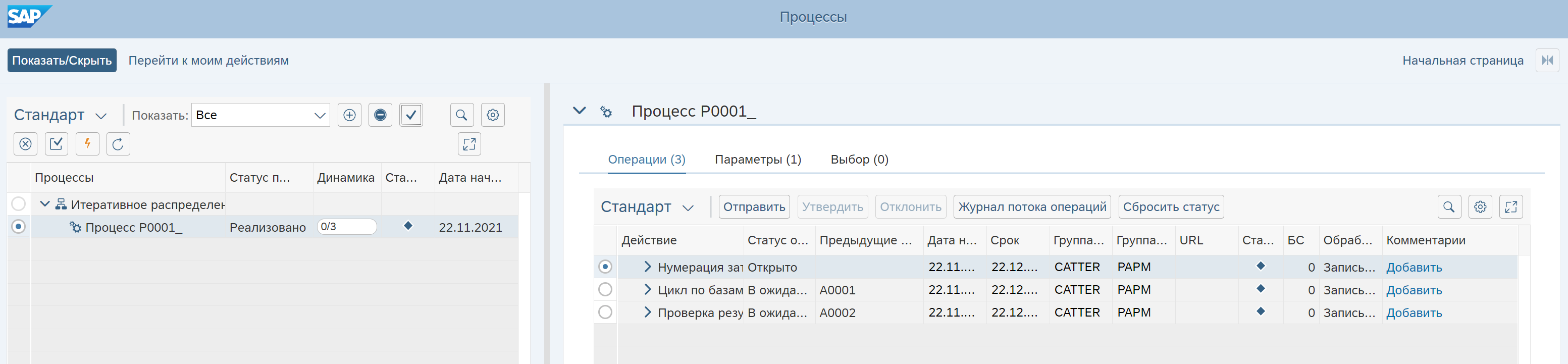
Further, you can carry out the execution of operations, control and approval of the result is carried out according to the assignment of users to groups. A user not assigned to an execution group cannot start the operation.
Execute process operations
There is a separate FIORI application for viewing process reports:

The application shows ongoing operations to be performed or I/O operations to be started:

Here you can perform the operation itself, send it for approval using workflow, approve or reject the result upon approval, view workflow data.
I/O operations can be run to get reports:

in the form of diagrams

or in tabular form.
You can also go to the data entry form for editable queries:

There is also an option using the Analysis for Excel add-in:

More information about queries and the ability to edit indicators can be found in the article. here.
Reporting
There is a separate FIORI application for viewing process reports:

The application shows on one screen the result of all reports on the process in real time:

Another example from SAP Standard Business Content shipped with PaPM:

For data-entry reports in this application, you can enter measures using the user interface and update the calculation to simulate “what if…”:

Application Monitor
When generating SQL scripts, a code is embedded that allows you to save detailed information about the progress of its execution in the application log. Application Monitor shows this information:

Now that’s a perfectly reasonable conclusion…
Output
Probably, in certain situations, when the calculation algorithms are stable and the same code is executed from time to time, native development in SQL will be easier, faster and cheaper than PaPM. But if modeling is required, when calculation algorithms change and it is necessary to flexibly manage the calculation logic, calculation input conditions, then one cannot do without a tool for managing calculation elements (stored procedures), the sequence of their execution, organizing launches, monitoring progress and processing results. Creating it yourself is a waste of effort, time and money, while SAP PaPM is already there.




