What is Big data engineering, and how to develop in this area

Big Data Engineering has emerged as a separate profession quite recently. And even large companies very often confuse what this specialist does, what his competencies are and why he is in the organization at all.
Therefore, in today’s article we will figure out who Big Data Engineer is, what he does and how he differs from Data Analyst and Data Scientist. This guide is suitable for people who want to work with big data and are looking at the profession in general. And also for those who just want to understand what data engineers are doing.
Who is Big data engineer
The tasks that a big data engineer performs are part of the machine learning development cycle. His work is closely related to data analytics and data science.
The main task of a Data Engineer is to build a data storage system, clean and format them, and also set up the process of updating and receiving data for further work with them. In addition, the data engineer is directly involved in the creation of information processing and machine learning models.
A data engineer is in demand in a wide variety of areas: e-commerce, finance, tourism, construction – in any business where there is a flow of various data and the need to analyze it.
For example, when developing a “smart” home. The creation of such a system requires reading and processing data from IoT sensors in real time. It is imperative that data be processed as quickly as possible and with minimal latency. And even if the system crashes, data must continue to accumulate and then be processed. Designing a system that meets these requirements is the data engineer’s job.
On the technical side, the most common tasks for a data engineer are:
Development of pipeline data processing processes. This is one of the main tasks of the BDE in any project. It is the creation of the structure of processing processes and their implementation in the context of a specific task. These processes make it possible to carry out ETL (extract, transform, load) with maximum efficiency – the extraction of data, their transformation and loading into another system for further processing. In static and streaming data, these processes differ significantly. For this, the most often used frameworks Kafka, Apache Spark, Storm, Flink, as well as cloud services Google Cloud and Azure.
Data storage. Designing a mechanism for storing and accessing data is another frequent task of data engineers. You need to choose the most appropriate type of database – relational or non-relational, and then configure the processes themselves.
Data processing. The processes of structuring, changing the type, cleansing data and searching for anomalies in all of these algorithms. The preprocessing can be part of either a machine learning system or a data pipeline system.
Data infrastructure development. The data engineer takes part in the deployment and configuration of existing solutions, determining the required resource capacities for programs and systems, building systems for collecting metrics and logs.
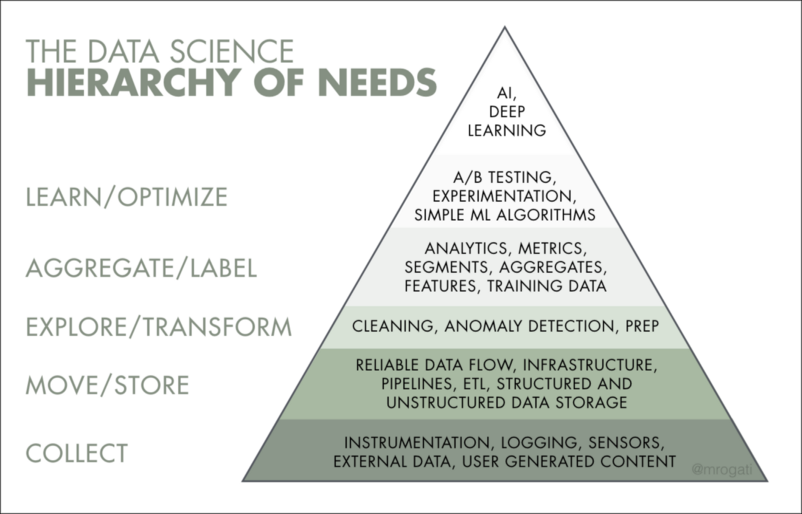
In the data hierarchy, the engineer is responsible for the bottom three steps: collecting, processing, and transforming data.
What Data Engineer Should Know
Data structures and algorithms;
Features of information storage in SQL and NoSQL databases. The most common: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Oracle, HP Vertica, Amazon Redshift;
ETL systems (BM WebSphere DataStage; Informatica PowerCenter; Oracle Data Integrator; SAP Data Services; SAS Data Integration Server);
Cloud services for big data Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure;
Big data clusters based on Apache and SQL engines for data analysis;
It is desirable to know programming languages (Python, Scala, Java).
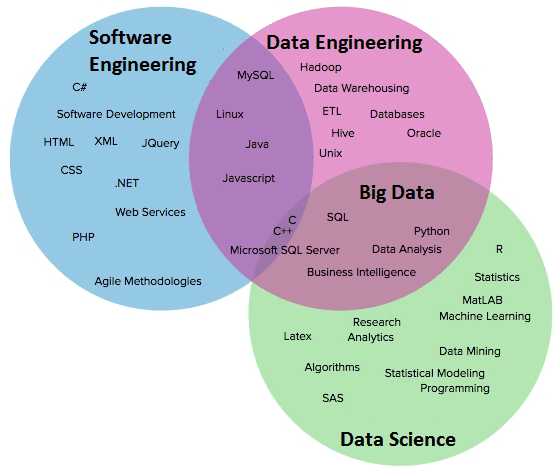
The skill stack of a big data engineer partially overlaps with a data scientist, but in projects they rather complement each other.
The Data Engineer is stronger at programming than the Data Scientist. And that, in turn, is stronger in statistics. The scientist is able to develop a prototype data processing model, and the engineer is able to qualitatively translate it into reality and turn the code into a product, which will then solve specific problems.
An engineer does not need knowledge in Business Intelligence, but experience in software development and cluster administration will come in handy.
But even though Data Engineer and Data Scientist must work as a team, they do have conflicts. After all, a Scientist is essentially a consumer of the data provided by an engineer. And competently established communication between them is the key to the success of the project as a whole.
Pros and cons of being a big data engineer
Pros:
The industry in general and the specialty in particular are still very young. Especially in Russia and the CIS countries. The demand for BDE specialists is growing steadily, and more and more projects appear that require a big data engineer. On hh.ru, as of the beginning of April, there are 768 vacancies.
So far, the competition for the position of Big Data Engineer is several times lower than that of Data Scientist. For specialists with experience in development, now is the most favorable time to move into a specialty. Learning a profession from scratch or almost from scratch is also quite good (with due diligence). The growth trend of the market as a whole will continue for the next few years, and all this time there will be a shortage of good specialists.
The tasks are quite varied – there is a routine here, but it is quite small. In most cases, you will need to be creative and get creative. Lovers of experimenting here is a real expanse.
Minuses
A wide variety of tools and frameworks. Really very large – and in preparation for the task, you have to seriously analyze the advantages and disadvantages in each specific case. And for this you need to know quite deeply the capabilities of each of them. Yes, yes, exactly each, and not one or several.
There are already six platforms that are common in most projects.
Spark Is a popular distributed computing tool with a rich ecosystem and libs that can be used for batch and streaming applications.
Flink – An alternative to Spark with a unified approach to streaming / batch computing, has become widely known in the data development community.
Kafka Is now a full-fledged streaming platform capable of performing real-time analytics and processing data at high bandwidth. ElasticSearch Is a distributed search engine built on top of Apache Lucene.
PostgreSQL Is a popular open source database.
Redshift Is an analytical solution for databases / data warehouses from AWS.It’s hard to break into BD Engineering without a background in development. There are similar cases, but the basis of the profession is made up of specialists with development experience of 1–2 years. And confident knowledge of Python or Scala already at the start is a must-have.
The work of such an engineer is largely invisible. His decisions are at the heart of the work of other specialists, but at the same time they are not directed directly at the consumer. Their consumer is Data Scientist and Data Analyst, which is why it happens that the engineer is underestimated. And it is almost impossible to change the real and objective impact on the final product. But this is fully compensated by the high salary.
How to become a Data Engineer and where to grow
The data engineer profession is quite demanding on the background. The backbone of the profession is made up of Python and Scala developers who have decided to leave for Big Data. In Russian-speaking countries, for example, the percentage of these languages in working with big data is about 50/50. If you know Java, that’s fine too.
A good knowledge of SQL is also important. Therefore, Data Engineer often includes specialists who have already worked with data: Data Analyst, Business Analyst, Data Scientist. It will be easiest for a data scientist with 1–2 years of experience to enter the specialty.
Frameworks can be mastered in the process of work, but at least a few things are important to know at a good level from the very beginning.
Further development for Big Data Engineers is also quite diverse. You can go to related Data Science or Data Analytics, data architecture, Devops specialties. You can also go into pure development in Python or Scala, but this is done by a rather small percentage of specialists.
The prospects for the profession are simply colossal. According to the data Dice Tech Job Report 2020Data Engineering is showing incredible growth rates – in 2019, the profession market increased by 50%. For comparison: the standard growth is 3-5%.
In 2020, the pace has slowed down, but still they are many times ahead of other industries. The demand for a specialty has grown by another 24.8%. And such rates will continue for at least another five years.
So now is just a great time to enter the Data Engineering profession with our course. Data Engineering and become a sought-after specialist in any serious Data Science project. As long as the market is growing so quickly, even beginners have the opportunity to find a good job.

find outHow to upgrade in other areas of working with data or master them from scratch:
Other professions and courses
PROFESSION
COURSES