The Internet is drowning in spam

Researchers have also noticed a deterioration in search quality recently.
The situation is so dire that users have to install special extensions like uBlacklistto block spam sites in search results:

Extension uBlacklist
For the sake of affiliate links and search traffic, spammers create fake blogs from fake personalities with meaningless generated texts to attract search traffic.

Modern blogspam. Fake blog from a fake person. Even the face itself appears to have been generated by a neural network. This Person Does Not Exist
Spammers penetrate any platform that is indexed by search engines.
Spam on Twitter and social networks, application directories, package managers
There is an assumption that in the near future LLM garbage will fill all possible voids where it is beneficial to use neural networks instead of people:
- film scripts (already a significant part of scripts for low-budget films are generated by LLM, including simple dialogues);
- pop music;
- literary works;
- articles in the media;
- posts on blogs and social networks.
- voice communication by phone (technical support, customer service).
Spam even reached NPM packages: by
25% of new packages in the second quarter. 2024 contains spam. The advertising campaign is especially noticeable
which offers financial rewards to open source developers, encouraging them, among other things, to clone other people's repositories and packages, and even generate meaningless code. There the reward depends on the contribution. That is, the more repositories, the more profitable. Hence the thousands of meaningless clones.

Distribution of financial rewards among open source developers using the Tea protocol, taking into account application dependencies, source
The platform itself encourages users to engage in this behavior by offering rewards (in points) for completing various tasks, including viral dissemination of information on social networks:

A similar situation occurred on Github, where The amount of spam has gotten out of control. It's mainly inhabited by crypto-spammers and scammers who publish a post with tags from many other, real users – and then quickly delete it. However, each Github user “tagged” in the post receives a copy of the text by mail. An original way to initiate a mailing campaign. It looks like this something like this:


If you search for current spam topics, you can find them in the comments to pull requests and bugs, these are hundreds of comments:

Unfortunately, Github does not have an effective spam filtering system, so promotional comments remain for many days or weeks rather than being deleted immediately. More garbage in the OpenAI application catalog (GPT Store) and other directories:

Spam penetrates literally everywhere. A stranger may even add events to your personal Apple, Google or Microsoft calendar. To do this, you just need to know the email address associated with your account if the “Add invitations from everyone” option is enabled in the settings:

It is ironic that even on the website of an independent search engine, which aims to rid search results of SEO spam, 99% of visitors are spam SEO bots.
How to protect yourself from garbage? No way. The method is simple: take content from trusted sources. Paid subscription, personal blogs.
By the way, Google recently came up with watermark technology for LLM texts. The idea is that when generating text, LLM selects tokens based in part on a cryptographic key. And someone who knows the key can identify and prove the use of the key in creating a particular text. Historically, watermarking texts causes two difficulties:
- their detection requires a relatively large amount of text;
- The watermark is not very resistant to editing after generation.
Google's version of watermarks looks good: it is detected even in small texts of 200 tokens, that is, about three to four paragraphs of standard text.
The algorithm called SynthID-Text (shown below) consists of three components, highlighted in blue: a random seed generator, a sampling algorithm, and a scoring function. They are used in text generation and watermark detection.

When generating SynthID-Text watermarks, the Tournament sampling algorithm is used, here's how it works:

The number of spam texts generated by LLM is growing exponentially. And the day is already approaching when there will be more generated garbage on the Internet than original content written by humans.
Experiment on 20 million generated neural network texts Google Gemini with watermarks showed no deterioration in the quality of output. Specialists predictthat all major LLM developers will implement a watermarking feature in their output.
Junk advertising surrounds us everywhere on the Internet, and even ad blockers such as uBlock Origin do not always save us. For example, the YouTube website tries to detect such blockers and bypass them, and also introduces “unmutable” advertising in different places of the video. In addition to this, Google itself is preparing to release a new version of the Chromium browser, in which uBlock Origin will stop functioning. And many other browsers, except Firefox and Safari, are based on the Chromium engine.
So, in order to block ads, you will have to return to Firefox or Opera, which promises save uBlock Origin functionality in full.
Phone calls. They deceive the smartest
Voice communications are also clogged with robocalls, spam and scams. It feels like hearing a live person on the phone will soon be a great success: always and everywhere the phone is answered by chatbots with speech recognition and other AI agents that may or may not switch you to a live operator. They say that there are special keywords (or obscene language) that help to quickly disable the automated program and attract a live operator.
According to experts, in the United States last year, 55 billion robocalls to citizens' phones. This is the same spam, only over the phone, perhaps even interactive, with speech recognition and primitive dialogue:

A proposal has already been sent to the US Federal Trade Commission introduce liability and limit robocalls without the recipient's consent. There is an idea to also introduce liability for advertising SMS. In addition, the United States recently introduced a mandatory “one-click” procedure for unsubscribing from any advertising mailings. This probably applies to advertising calls, SMS and other types of spam.
In addition to robotic spam, traditional social engineering continues to be used over the phone to lure a person out of personal data, gain access to his account, or convince him to transfer money. Calls allegedly from the police are popular; in Belarus, calls from the KGB. Fraudsters manipulate citizens' fear of government agencies. In a conversation, they do not leave a person time to think. The main thing is speed; the victim is forced to quickly react and act. For example, in Turkey, according to this scheme entire call centers operate with dozens of operators who are deceiving thousands of Europeans. Money siphoning operations are taking place on an industrial scale.
Research shows that most often young people aged 34 years become victims of scammers (clinical psychologist Ksenia Yagur spoke about this in a recent film with Yandex 360 experts about cyber fraud. Apparently, the smarter a person is, the easier it is to deceive him, because he is more confident in his own intelligence than a stupider relative who will simply hang up the phone without entering into discussions with the scammer.
Methods to combat email spam
Spam is now not only advertising, but also a threat. The ratio of fraud to junk in email spam is approximately 50/50.
Fraudsters are coming up with new ways of phishing and social engineering. For example, from recent inventions:
- Letters from government services asking for clarification of data
- Fake reply to your letter (non-existent or real)
ChatGPT too
helps bypass anti-spam filters
mail providers. But AI is used on both sides.
According to the Yandex 360 technical specialist from the above-mentioned film, 90% of all spam filtering work is now done by AI. For security reasons, a small part of the supervisory work was left to the person on duty who monitors mail traffic. In the event of a security breach, as last New Year (30 million spam emails), he promptly convenes a meeting of two to four programmers to work out and implement changes to spam filtering algorithms.
Using Spam Defense technology in Yandex.Mail, spam filtering occurs as follows, step by step:
- The mail message arrives to the server in the format
.eml - Basic SPF and DKIM check is carried out
- Checking against a list of trusted IP addresses
- Message parsing, feature analysis (about 10 thousand)
- Submitting features to the input of a machine learning system
- Obtaining the result of ML analysis in the form of a numerical coefficient that determines the probability of spam (in the mail interface this is reflected by a green, yellow or red “Spam” indicator next to the letter)
According to the representative, since the beginning of the year, over 66 billion letters have passed through their service, of which more than 16 billion are designated as spam. Probably, other effective spam filtering services have approximately the same percentage and operating principles as Gmail or Yahoo.
SPF, DKIM and DMARC are the main methods of protecting against email spam.
SPF, DKIM and DMARC
is a text entry in the TXT record of the DNS domain. It contains a list of servers that have the right to send letters on behalf of this domain and a mechanism for processing letters sent from other servers. This is an effective protection against phishing. An SPF record will prevent an attacker from sending emails from your domain, as was popular in the 90s. One type of phishing is essentially destroyed in the bud.
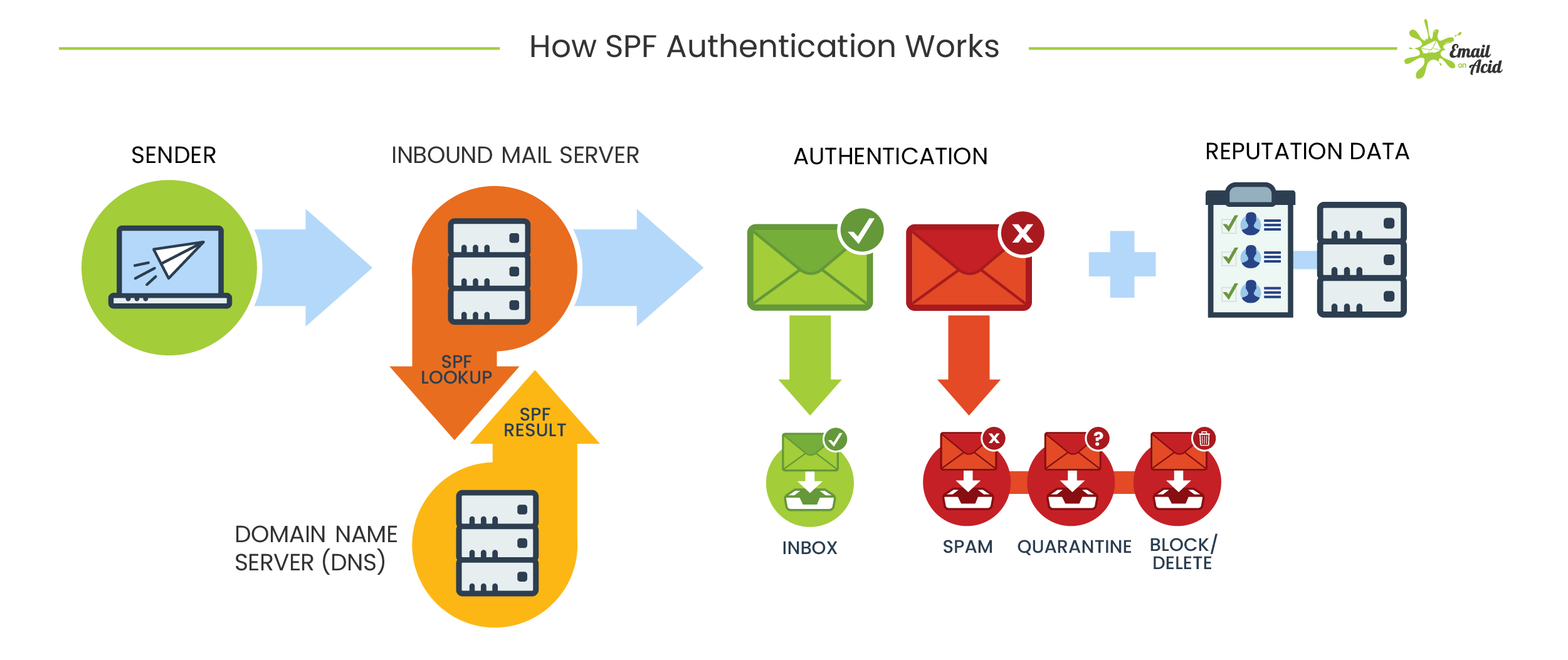
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) – a method of authentication of postal items that protects against counterfeiting (spoofing) sender's address using a digital signature.

DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication) — a technical specification for identifying sender mail domains based on the rules and characteristics specified on the recipient's mail server. This is specifically an anti-spam technology. DMARC provides mechanisms for the exchange of information between the sender and recipient about the quality of spam filtering and phishing attacks. For example, if you represent a sending domain and publish a DMARC record requesting information, you can receive statistics from all recipient domains that also support DMARC about all mail that arrives with a return address from your domain. DMARC policies are published in the Domain Name System as TXT resource records and contain instructions on what the receiving host should do with non-compliant messages received.

By the way, since February 2024, Gmail and Yahoo have tightened the rules for incoming letters (Gmail ad, Yahoo ad).
Three key changes for inbox that came into effect in 2024:
- Email authentication. Senders must verify the sender's identity using standard SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols.
- Easy unsubscribe. For bulk emails, senders should embed a one-click unsubscribe link in emails so that recipients can easily unsubscribe.
- Only emails that users need. Gmail and Yahoo have taken spam monitoring seriously, and senders must ensure that the number of emails sent does not exceed the 0.3% threshold.
Published on the Google website
How to best implement DKIM authentication for your domain. Today, SPF and DKIM support is the absolute minimum for outgoing emails, otherwise Google will send the emails to the Spam folder. For DMARC you need to implement at least the field
p=none
.
Unfortunately, the battle against spam is far from over. Cunning scammers are finding new ways to bypass any protection, make some money through affiliate programs, selling junk goods or banal fraud.
People's thirst for money is simply ineradicable, so we will have to live with this problem for many more years, and maybe forever, as long as human greed exists.
But if you set specific tasks, they can be solved at least partially. For example, we can effectively combat specifically postal spam. Digital signature for domains, white lists of verified addresses, encryption of letters – this is a fairly reliable set of technologies that you can rely on.
Of course, tightening security sometimes leads to false positiveswhen respectable domains end up on blacklists. Nowadays, it is almost impossible to send letters from your own mail server and domain, as it was in the 90s: large providers will simply block all your letters, regardless of their content and quantity. To break through all levels of spam defense, you need to comply with all the requirements of major email providers (see. higher) and constantly check your domain and IP address against blacklists:

New specifications are currently being developed to help address these issues. For example, the new standard ARC (Authenticated Received Chain) in addition to DMARC handle situations in which the latter fails. For example, it solves the problem of DKIM signatures in mailing lists.

And its logo is cute.





