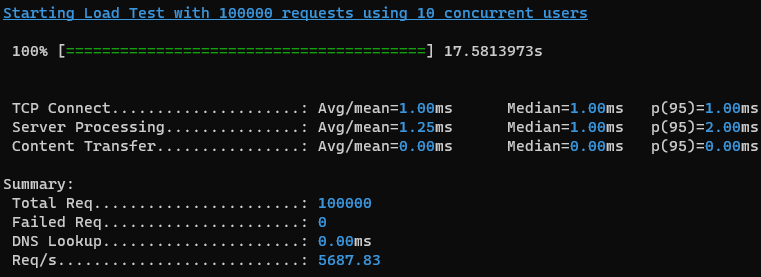
Similarities and differences between Wi-Fi 6 and 5G
What’s better? Who cares? As 5G comes, WiFi 6 will no longer be needed.
Very reminiscent of childhood with pressing topics:
Who is stronger than a whale or elephant?
Which actor is stronger than Van Damme or Schwarzenegger?
My kung fu is stronger than your karate!
I decided to share brief theses for educational program in the spirit of the 20s of the last century.
Disclaimer: The article does not claim to be comprehensive and fundamental.
What is similar?
The same basic technologies:
1) Wi-Fi 6 and 5G use orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) technology, which was first used in LTE networks.
2) In the Wi-Fi 6 network, subcarrier frequencies appeared for the simultaneous transmission of user data. In addition, multi-user MIMO systems (MU-MIMO) use Wi-Fi 6 to increase the bandwidth and number of connected subscribers for each access point four times.
In the environment of telecom operators Massive MIMO technology is used, which allows using up to 128 spatial streams.
Differences between Wi-Fi 6 and 5G:
Various application scenarios:
Wi-Fi 6 is a wireless technology that is suitable for indoor use. Due to limited resources in terms of spectrum and power, Wi-Fi 6 is not applicable to external long-distance coverage scenarios.
5G spectrum planning and management is carried out by SCRF based on the issuance of licenses for spectrum resources.
Let us leave out of the way the struggle for a frequency resource between business and government agencies.
For external use, the influence of interference is extremely small, so the use of 5G is quite logical.
However, indoors, the high frequencies (from 24 GHz to 52 GHz) used by 5G are highly susceptible to the attenuation effect, and in order to use 5G you will have to plan a very difficult deployment scenario.
An obvious advantage – Wi-Fi over 5G is the ease of deployment and further support in indoor coverage scenarios.
So it turns out that Wi-Fi 6 (mainly, although there are interesting applications outside) is used for campus networks of enterprises and high-density access indoors.
But the 5G place is most interesting in:
- voice solutions (Vo5g);
- data transfer scenarios;
- IoT infrastructure in Smart Cities.
Various methods of working with the spectrum:
The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi spectra are not licensed for indoor use. For their use, there is no need to apply for the frequency spectrum or register as a telecom operator.
Having chosen a Wi-Fi environment, enterprises can use the spectrum for free in wireless networks of WiFi 6 standard at a speed of 10 Gb / s.
Outdoor application, adjustable in the 5GHz band.
Read more here – https://digital.gov.ru/ru/appeals/faq/366/
For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), using their own 5G infrastructure and deploying 5G base stations is simply financially impractical.
Various costs:
Deploying Wi-Fi networks is very simple. As Wi-Fi access points become smarter (for example, Huawei access points use smart antennas and SmartRadio radio channel calibration technologies), planning and maintaining Wi-Fi networks becomes seriously easier than before.
Sometimes even without the involvement of professional engineers, which were previously required even in simple scenarios.
Note that complex and responsible implementations still require careful radio planning and radio modeling of a wireless network by professional engineers and architects.
5G wireless networks always require careful planning, modeling and controlled implementation at all stages of the project, both from scratch and when expanding the coverage area of the Communication Operator.
Thus, the total cost of starting the network varies by orders of magnitude.
Various ways to popularize 5G and Wi-Fi 6 terminals:
The cost of promoting Wi-Fi 6 terminals is lower. Updating used Wi-Fi 5 terminals to Wi-Fi 6 terminals requires updating the chipset on the end device, without the need to change the designed wireless architecture.
Portable terminals can even get started quickly in Wi-Fi 6 via PCIe cards or M2 slot.
The transition from non-5G terminals to 5G terminals involves the redesign of end devices, increasing system complexity and overall costs. Although of course there are assumptions and exceptions.
Therefore, the use of Wi-Fi 6 is preferable for end devices that were not going to support 5G, such as printers, electronic boards, intelligent building management systems, projection televisions and telepresence systems.
Interaction between Wi-Fi 6 and 5G:
5G networks have some limitations, for example, the high cost of indoor coverage and the inability to update old devices.
Wi-Fi 6 technology solves the problems associated with high bandwidth, high capacity and low latency in indoor coverage scenarios.
With these advantages, Wi-Fi 6 is suitable for key applications requiring high bandwidth and low latency, such as VR / AR, 4K / 8K content, and Automated Driving Vehicles (AGV).
Thus, for enterprises, Wi-Fi networks 6 and 5 G can interact with each other in most scenarios in synergy mode to achieve an optimal access and coverage ecosystem.
For some industrial scenarios, such as oil fields, coal mines and AGV-5G, it has unique advantages, including low latency and wide area coverage.
In scenarios with very high street density (for example, in squares and stadiums), the 5G network bandwidth will not always be able to satisfy user access requirements without adding a significant number of base stations.
In this case, high-density Wi-Fi 6 is a cost-effective solution for accessing a large number of users and high-density terminals.
Conclusion:
Despite similar physical technologies, the scope of Wi-FI 6 and 5G varies according to industrial scenarios, as well as the cost of implementation and ownership.
Therefore, the conclusion “who is cooler” will be better illustrated with a picture!

I hope that this material was useful and helped to understand the main key elements of similarity and differences of these technologies.