How to Create the Perfect SEO Structure the First Time: 5 Steps
Hi all! My name is Artem Pervukhin, I am the production director of the Kinetics performance agency. In the company, we have been helping businesses to successfully move online for more than 15 years, and we boldly share our experience and best practices.
In the last article we have analyzed why it is important to build a competent website structure from the very beginning. Here we will delve into the specific stages of development – how to create a structure from scratch that will immediately show itself well in battle. After all, you must admit that it is much easier to spend time and money on setting up at the very beginning than six months later to find many errors, poor indexing and ask specialists to fix it? After all, the second option will cost you many times more!
Get ready to plunge into promotion with me, step by step creating an effective SEO framework using the example of an online battery store. And read the article 😉
Step 1. Collect marker requests
At the first stage, we manually collect requests that most fully reflect the company’s activities and assortment. They are called markers and cover the entire search demand and the future site. The collected information is entered into the mind-map.
If the site sells bicycles, you can use the general marker “bike”. And if we are talking about a site with a wide range, for each section you need to choose your own markers.
For an online store of batteries, you can take the markers “Battery”, “AKB”, since these are the main products of the company. A more difficult option would be to select markers throughout the site structure when they are divided into groups and subgroups:

You can use the free service bukvarix.com. We indicate in the search line our query “batteries for UPS” and we get several thousand matches at the output.
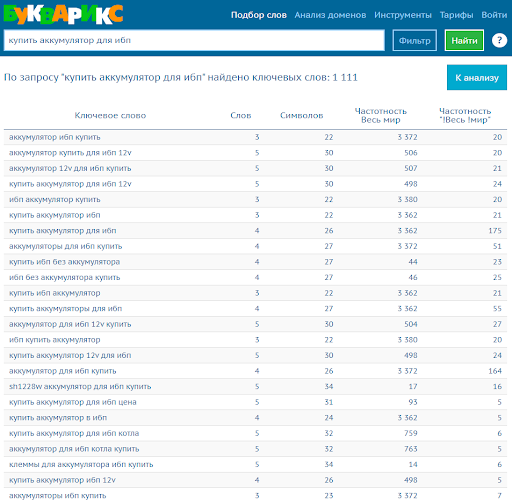
For clarity, I will take a small piece from the unloading in order to further break it into groups. We get the following list:
After collecting the markers, we enter everything into the mind-map and further expand the marker requests. This shows which categories are in demand and which phrases should be in them. In the future, this will help you to move effectively – in order to receive traffic and collect applications.
Step 2. Clean up garbage and cluster
We clean the collected file from non-thematic, erroneous phrases, mentions of competitors. We remove queries mentioning cities in which the client’s website does not work. The logic is simple – if we don’t sell something, then we don’t need these requests.
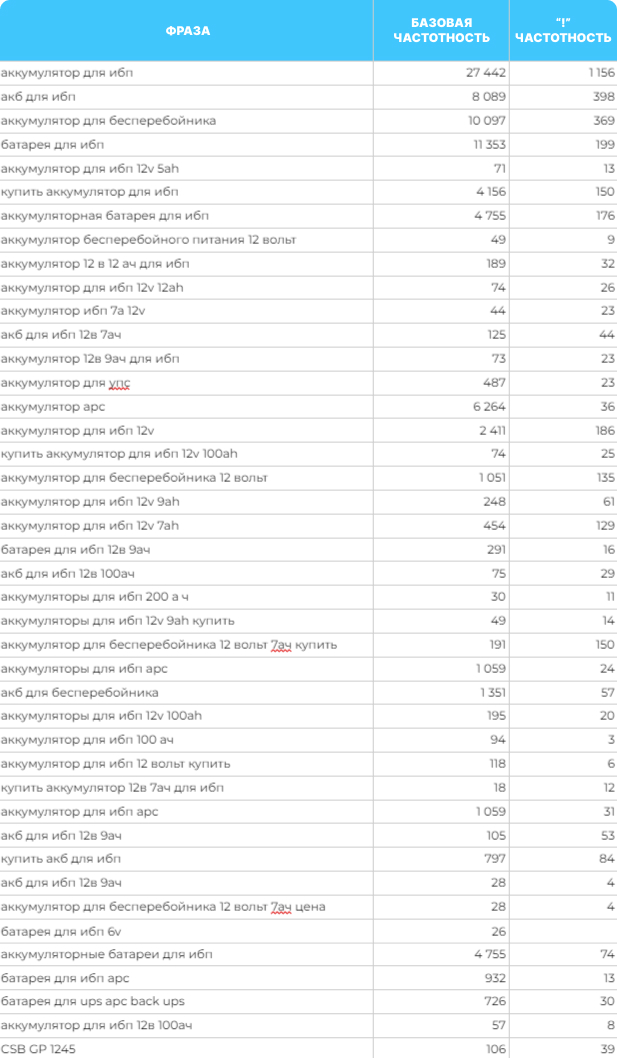
From here, we also need to remove implicit duplicates – requests from words and word forms that duplicate the main requests, but lose them in frequency.
Then we distribute requests into groups according to intent and search results – this is called clustering. The trick is that “acb for 12 V”, “acb for 6 V”, “acb for [определенный бренд]” should be promoted in different ways, so we group repeated user intents.
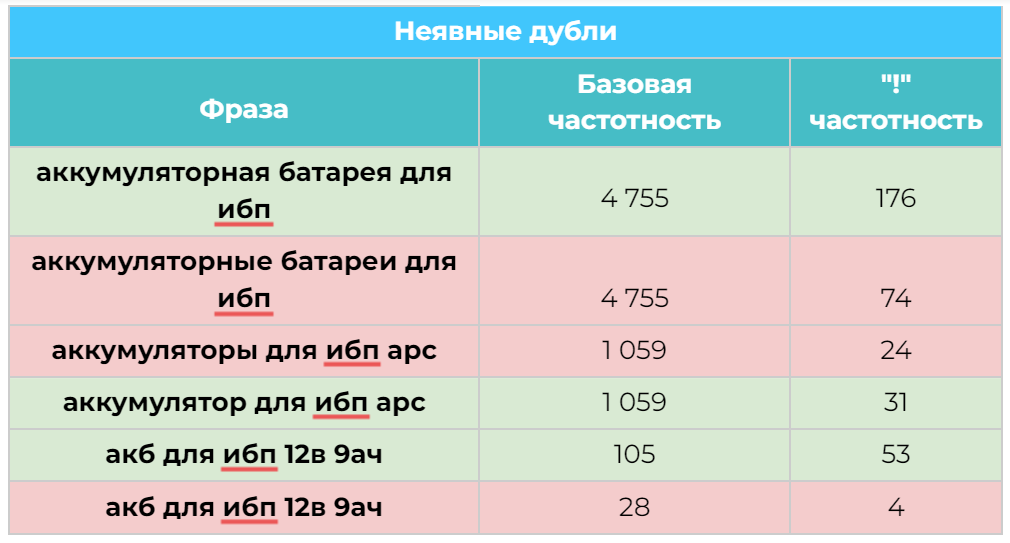
After that, we need to separate category requests from product requests. despite queries that are similar in meaning, they should be located on different landing pages.
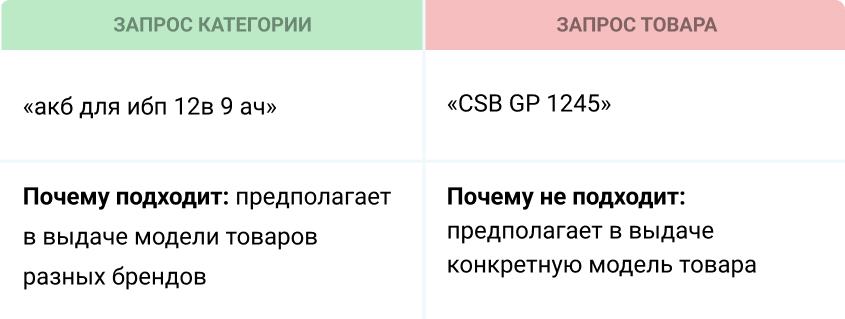
In order not to do this manually, we use clustering services (Key Assort, Key Collector) and get requests distributed into groups. If you want to try it now, use Kulakov’s free service.
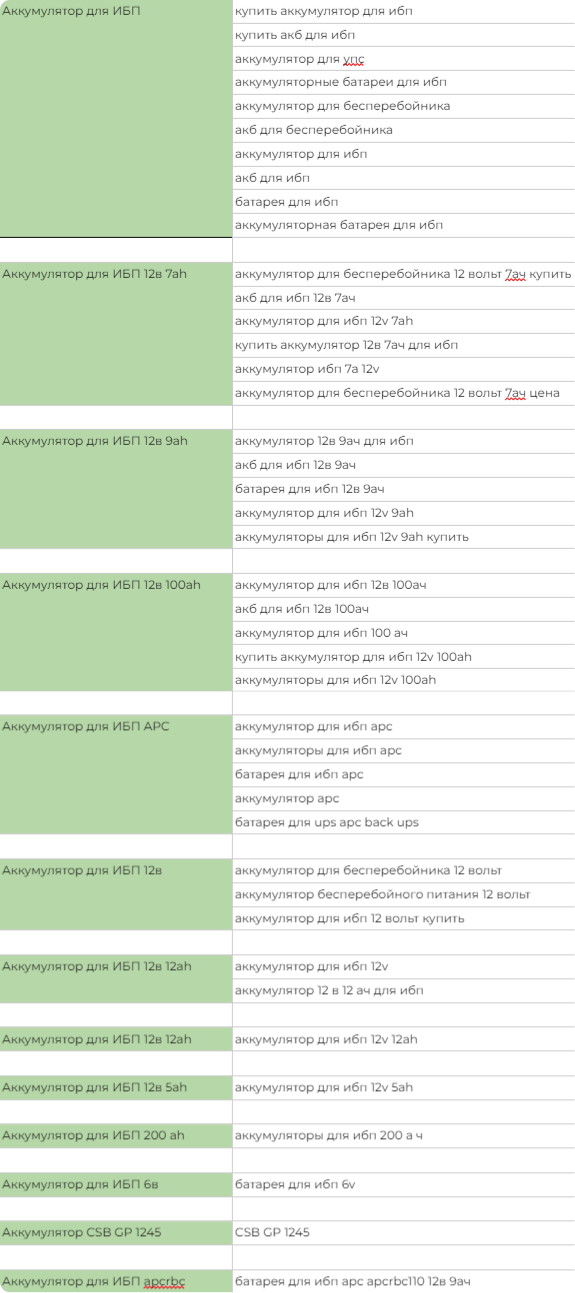
In our case, there were 12 groups.
Step 3. We look at competitors and plan to do better than them
It is important to correctly assess the demand and select competitors. Usually, well-known market players are named at the meeting, with whom it will be impossible to compete – aggregators, marketplaces, niche leaders. And this is a big mistake.
Even if their sites have structural flaws (there is no section or two clusters are merged), they are more than compensated by trust metrics earned over many years. Therefore, it is necessary to focus on direct competitors.
Competitor – not the one who bypasses you offline, but the one who is the same as you in terms of scale and assortment, but better in visibility (he is in the top 10, but you are not). These are the ones we find by marker queries in the top 10 and suggest ousting them.
After we have collected suitable competitors, we look at their structure and landing pages. It is important to find useful chips from competitors and use them at home. Now I’ll show you how it works.
For example, we look at our project on the page “acb for UPS”. There is no nesting in the structure. Thus, the user on the page will have to search for the necessary product for a long time. Therefore, we need to create additional landing pages in order, among other things, to bypass sites where such pages exist.
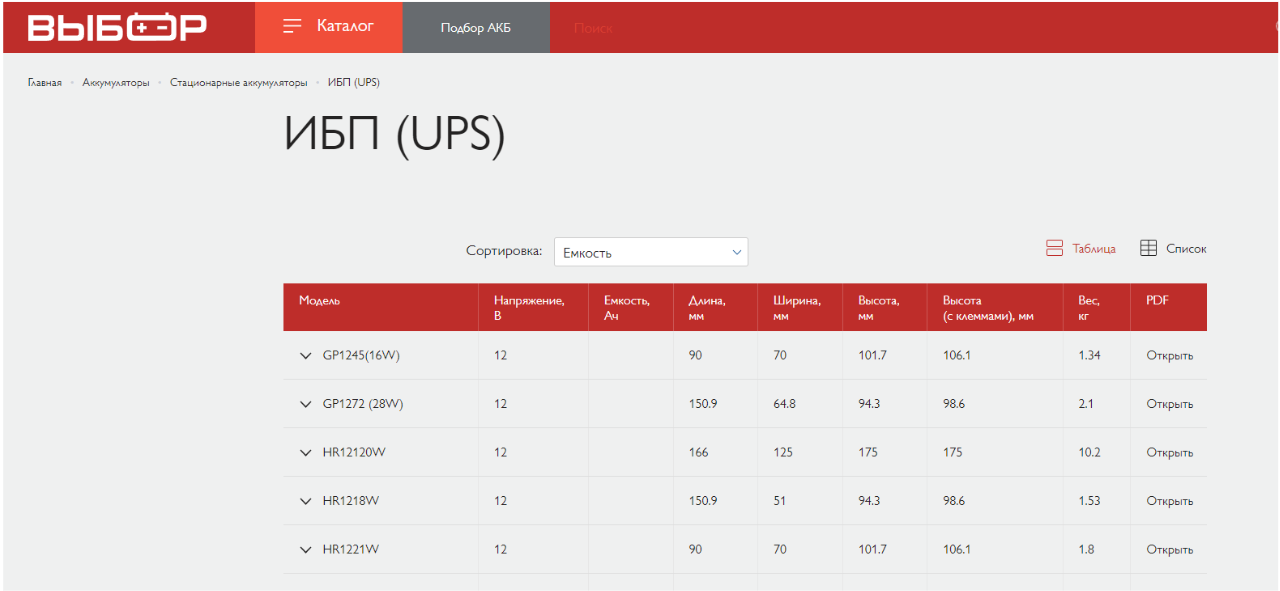
While competitors in the category “Uninterruptible power supplies” have additional subcategories – by power, brand, topology and design.
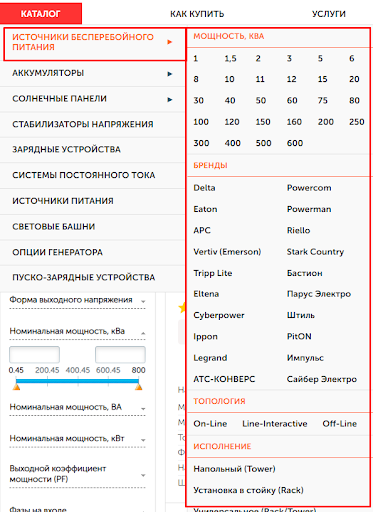
By this stage, our mind-map is growing more and more, where we write sections, categories and subcategories of our future site, as well as structural elements that attracted us from competitors.
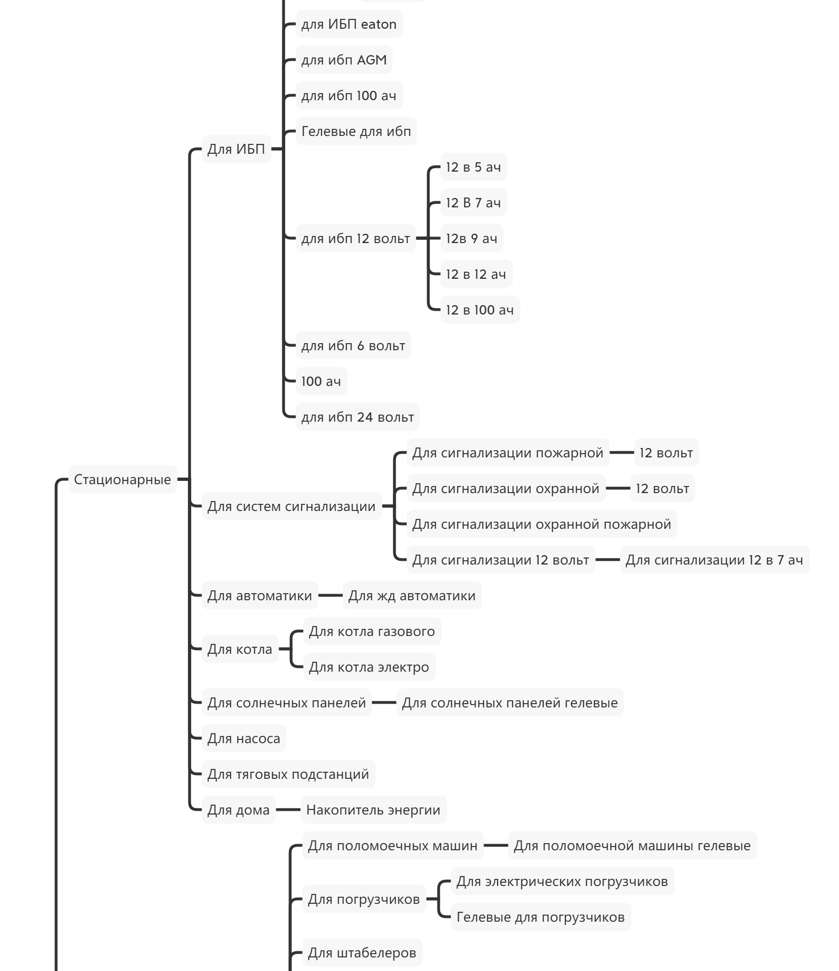
Step 4. We form the semantic core
It’s time to build a core in all categories based on the mind-map. To do this, we use the Key Collector service.
In general, the topic of forming a semantic core is a big one – for a separate article. If you are interested, let me know in the comments, I will publish the article.
The finished semantic core looks like a big picture with a lot of hierarchies and phrases.
This is how we understand all the variations of requests that users are looking for in our subject and what applies to our site.
Step 5. Upgrading site elements
When the formation of the main structure is over, we proceed to polishing – establishing effective interaction between the user and search robots with the site. To do this, we create breadcrumbs, pagination and much more. About everything in order.
breadcrumbs
These are additional occurrences on pages by category names. They have several obvious advantages:
make pages more convenient – it is easier for users to navigate in sections and go to general categories;
participate in internal linking – help distribute link juice.
Pagination
A large number of products or blog articles are much more convenient to view if they are divided into pages. Displaying a limited number of elements on a page is called pagination.
Webmasters arrange pagination using numbered pages, a range of numbers, an alphabetical list, where each page is a selection of products starting with a certain letter, and other methods.
Tips for setting up pagination:
Use pagination with numbering, if the site has more than a hundred products, there are many articles, and their number is growing.
Better yet, give users two viewing options: it is convenient for someone to view products by switching pages, and for someone – to load them by pressing the “show more” button.
Do not prohibit page indexing with the noindex tag, as this is one of the ways to the product card. Otherwise, the bot will not be able to get to the product page, and this worsens commercial factors.
Do not duplicate the text of a section on its pagination. So it will not be repeated on all pagination pages, and you will not reduce the uniqueness of the content.
Filters
Filter is a set of parameters that allows you to narrow down a large assortment to the desired selection.
Filters simplify the search for a product or service and contribute to the creation of landing pages for SEO promotion. An important condition is that only pages with filters that are in demand should be generated. Otherwise, it will be a junk page that search engines should not see.
Advantages of filters:
Increasing quality organic traffic. If users often ask for a specific color of a product, then it will be convenient for them to see this characteristic at the beginning of the filter.
Ease of promotion. Everyone wants to advance on high-frequency queries, while all the profit is in mid-range and low-frequency queries – users with low-frequency queries usually know what they want and are more likely to make a purchase.
Ease of generation. It’s easy to create filter pages for catalogs from a template and apply it to several categories – you get unique pages.
Improvement in behavioral factors. When the filters are well-designed, it is easier for users to interact with the site and find the right product or service. The time of the visit and the depth of viewing the site increases, the bounce rate decreases.
Tagged pages
Filters that allow the user to filter out unnecessary goods are very important and convenient. No one wants to dig through the mountain of goods in search of the right one!
Tagged pages will come to the rescue, which group products based on specified properties.
Tagged pages – These are peculiar pseudo-categories in which goods are combined according to narrow criteria. They allow you to quickly sift through the sample without adjusting the filter.
Each combination of popular characteristics for a specific request is a separately created page. It gets into the index and is ranked by it first.
For example, if a user enters “acb for UPS 12V” into the search string, and such a pseudo-category has been created in your store, most likely it will be in the top of the search results.

How do I know which pseudo-category to create? Learn the needs of the target audience through semantics. At this point, we already have a semantic matrix in our hands, from which it is clear what queries can be left for tagged pages. And if something went wrong and the query combinations were not worked out, go back one step and disassemble the semantic core.
And finally
You should think about the correct SEO structure even before the launch of the site – this will significantly reduce the cost of further edits.
And if you have any questions – write in the comments, I will answer;)