How Service Desk is changing in ITIL 4
We outline the main changes in the approach to Service Desk from the point of view of the authors of ITIL 4.
New features
As before, Service Desk is engaged in technical support: monitors and processes incidents, accepts service requests. But now many technical support processes are automated using interactive voice menus (IVR), robots (RPA) and chat bots. The load on the first line of technical support is reduced, Service Desk can deal with already higher-level tasks. For example, to act as an internal coordinator, helping colleagues and business.
Major changes:
- fewer phone contacts with users
- more work on the second line of technical support
- more opportunity to focus on enhancing CX (Customer Experience) when you need personal contact with the user.
Cooperation
No matter how effective the support service and its staff, problems will always arise that require the connection of other teams. For example, in a product company, developers must work closely with the support service to form a unified approach to users and customers.
Even if Service Desk is not required to solve complex technical problems, it still plays an important role in the provision of services, and colleagues from related departments should help her. Keep in mind that customer support affects the user experience and how the service provider is perceived by users.
Expanding Context and Skills
Support should delve into business processes and know the target audience of the supplier. It increases the value (Value Stream) not only through standard actions, such as registering user requests, but also by understanding how these standard actions fit into the business context.
Service Desk personnel require competence in a number of technical and business areas. Non-technical customer service skills, such as empathy, emotional intelligence, are also important. Service Desk personnel must use existing skills, people, and processes to manage incidents.
Communication channels
The support service uses various channels of communication with users. Each of the channels should be convenient for handling:
- phone calls, including IVR and conference calling;
- mobile applications;
- service portals;
- catalogs and knowledge bases;
- chats and chat bots;
- E-mail (in addition to traditional correspondence, artificial answers and machine learning are introduced for auto-answers to atypical inquiries and letters);
- service centers – where the physical presence of a specialist is required;
- SMS and social networks – for notification of incidents, communication with users and receiving calls.
Technologies
In order to ensure the high-quality work of Service Desk, various technologies are used:
- Intelligent telephony systems that integrate IP telephony, IVR and automatic call distribution;
- personnel management and resource planning systems;
- knowledge base;
- call recording and quality control;
- remote access tools;
- administration panel and monitoring tools;
- configuration management systems (CMDB);
- A remote (or outsourced) support service needs a more complex organization of work, including based on cloud solutions.
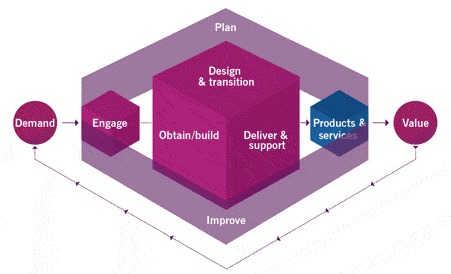
Contribution of Service Desk to ITIL 4 Value Chain
/axelos.com /
The figure shows the contribution of the support service to the value chain of the service from the point of view of ITIL 4. As you can see, Engage and delivery and support are a priority. Apart from planning (Plan), Service Desk is involved in all stages of the chain.
- Improvement (Improve). Support desk activities are constantly monitored and evaluated to continuously improve performance, and hence the value chain. For the same purposes, the support service collects feedback from users.
- Engagement. Support service is the main channel for tactical and operational interaction with users.
- Design and Transformation. Support is the main source of messages about new services and updates. Service Desk employees participate in release planning, testing, and support services early on.
- Get / Build (Obtain / build). Support staff are involved in the purchase of service components and equipment that are required to fulfill service requests and resolve incidents.
- Delivery and support (Deliver and support). Customer Support is the focal point for managing incidents and service requests.
The role of automation tools
The evolution of the Service Desk is impossible without a reliable technological base – ITSM / ESM solutions that take into account the best practices of ITIL 4. These solutions help automate the support service and quickly solve user problems using the following tools:
- request processing (Help Desk Ticketing);
- Workflow Management
- User Self-Service Portal (Self-Service);
- knowledge base (KMDB);
- reporting (Reporting).
Support service productivity and value are enhanced by integrating the basic Service Desk tools with other components of the ITSM / ESM system:
- configuration management database (CMDB);
- change management;
- monitoring
- asset Management.
Conclusion
Today, Service Desk is customer oriented. Support specialists require new skills and expertise. If earlier formal indicators were the main guideline, now positive user experience and understanding of one’s place in the value chain are much more important. Authors of ITIL 4 are called these changes are a “major cultural shift” for Service Desk.