ERP versus microservice approach: when can you launch your marketplace?

Large players in Russia who combine retail, distribution, online stores, most often think about creating their own marketplaces. It’s simple: the pandemic has been actively taking everyone online for a long time, no one wants to lose customers, so they begin to actively rebuild themselves to e-commerce trends.
And most of these companies have their own ERP system. The first thought that comes to them is to launch a marketplace on the current system. Which is a mistake. It is impossible to develop a full-fledged marketplace from an online store or an ERP system: an IT platform (in fact, the marketplace itself) must be created initially, where a company with its own products and an ERP system acts as a supplier like everyone else.
What systems does the marketplace include?
Marketplace is a complex, highly loaded IT platform, which can be conditionally divided into 4 main blocks: “buyer”, “seller”, “core and processing” and “finance”. Each of the blocks contains many small IT systems that are responsible for specific functions.
The first block includes a storefront, payment services, loyalty programs, customer CRM, support and a call center, as well as various customer experience stories to build personalized marketing and competent communication with the buyer.
The second logical block is associated with sellers on marketplaces. Unlike classic retail, it is important to set up a completely autonomous operation here. Sellers should have their own personal account, work on the API should be built, they should increase the assortment and turnover (you need a CRM and a document management system), working with the platform, in general, switch to fully automated processes.
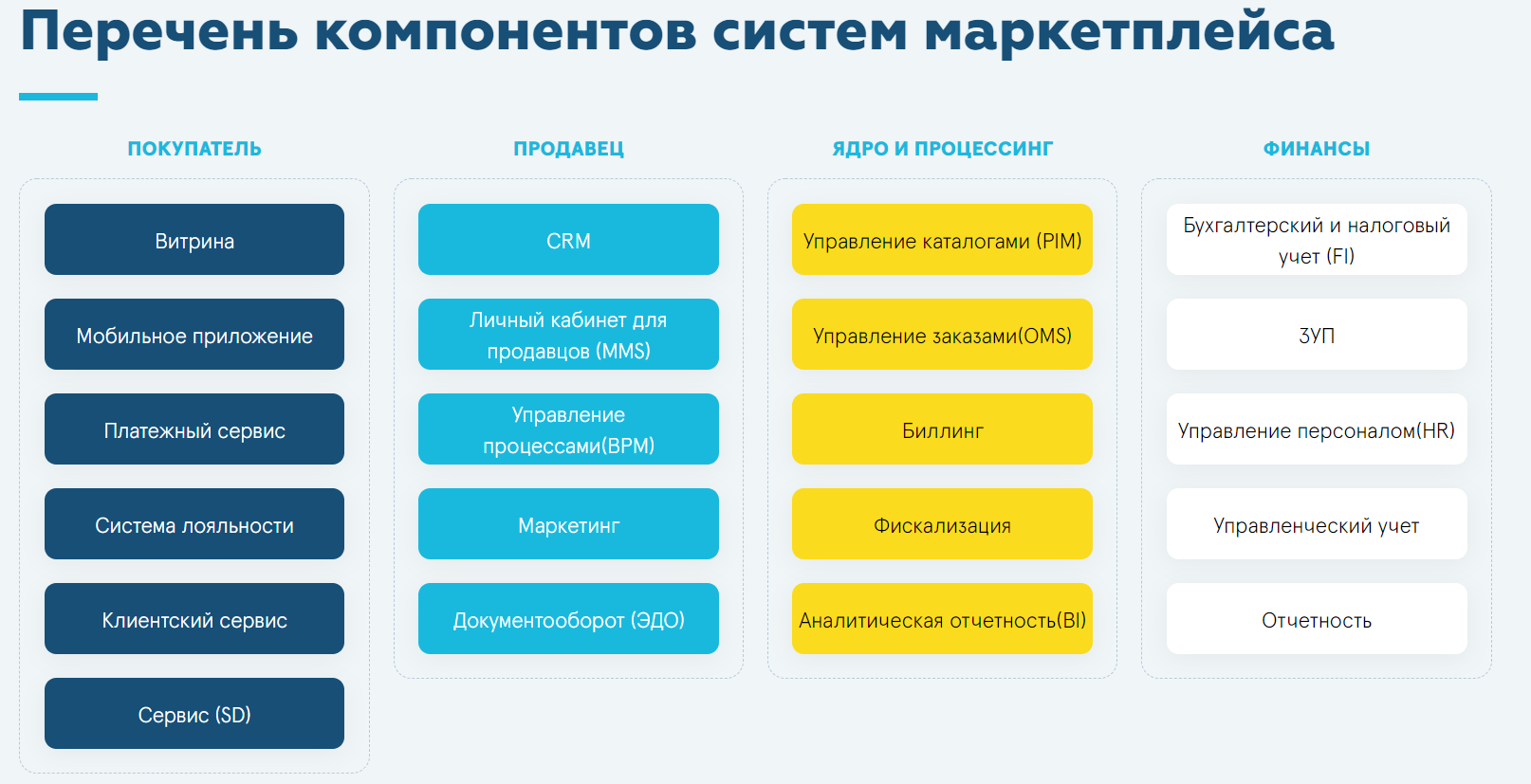
The third logical block “core and processing” includes a product management system (PIM), which is necessary for managing the rules for filling in product data, managing a product hierarchy, an order management system (OMS), which is ready to process a large number of transactions on the fly, as well as billing processes for solving issues of monetization, tariff scales, etc. The platform is completed by block 4, which includes components responsible for the financial side (accounting and tax accounting, ZUP, management accounting).
Which marketplace concept and strategy to choose
There are two main concepts:
-
commission trading is the most common model, when the marketplace does not redeem goods on its own, but acts as an agent and takes a specific commission for the sale, depending on the category;
-
direct purchase and sale agreement – a scheme when the marketplace, in fact, is just an intermediary between the buyer and the seller, who conclude a purchase and sale agreement between themselves.
And 3 main strategies for organizing a showcase:
-
“1 card = 1 seller”, which in fact resembles the model of any online store and is not particularly scalable;
-
“1 card = 1 best seller”, where only one best offer from the seller is shown (for prices and other parameters). For example, this is how Wildberries work;
-
“1 card = many sellers”, the most suitable strategy for creating an open format marketplace, where the buyer chooses the most suitable from a variety of offers, and the sellers fight for a winning place in the card itself. For example, Yandex.Market before integration with Beru.
In order not to get confused in the development process, first of all, you need to decide exactly on the concept and strategy.
The easiest way is to take a commission scheme, since for direct sales you need to cut the settlement system from scratch. Of the strategies, you should pay attention to “1 card = many sellers”, since there is room for development. The only difficulty here is the development of a back office, which includes:
-
accounting and tax accounting;
-
Management Accounting;
-
calculation of salary;
-
personnel Management;
-
reporting;
-
document flow.
To date, there are no ready-made solutions that can be implemented to instantly launch the platform. Part of the back-office tasks will be handled by 1C due to its flexibility and scalability. But in any case, some systems will need to be improved.
Minimum at the start: systems, content, customer relations, logistics
In MPV (initial version), to begin with, you should lay the following systems:
-
PIM (Product Management);
-
showcase (the site itself);
-
seller’s personal account (MMS);
-
order management (OMS);
-
warehouse management (WMS).
For a start, in most cases, this is quite enough. The rest will evolve already in the process, it is important that the architecture of the marketplace is created from small microservices that can be scaled. When working with content, there are two options: prepare in advance, for example, recruit content managers and bring them to the site yourself, or buy ready-made content from specialized companies.
When working with customers, you need to focus on systems such as:
-
the showcase (the face of your marketplace) should contain many options from different suppliers in order to interest the visitor;
-
payment services should include several types of payment so that the buyer has a choice, which will be a plus for the convenience of working with the marketplace;
-
customer support systems (for example, a call center that will receive requests on time);
-
to increase the average check of purchases, increase the share of repeat purchases and reduce the cost of attracting customers, you need to think over a loyalty program (bonuses, discounts, promotions).
As for logistics, at the start, everyone usually starts when the seller delivers goods to the warehouse of the marketplace in large deliveries, and not for each order separately. But the delivery from the seller’s warehouse to the architecture is better to be laid down immediately and further developed in order to expand the offers and optimize the workload of the warehouse.
How much to invest in development in the end, and when will it all pay off?
There is a key point here. When retail begins to transform into a marketplace, there is usually an imbalance in terms of financial investments. Most organizations start investing in premises, in a range of products and forget that a marketplace is primarily an IT company that needs a good team of developers and analysts.
Without creating the right IT infrastructure, no marketplace can exist. Therefore, the main investment priority is the development of the IT team, which will be able to comprehensively approach the issue of analysis, after which it is already worth starting the development.
There is no exact figure for how much all this will cost. Most often, the start of a small industry start-up starts from 10 million rubles, the average one – from 30 million rubles, and the giants can reach billions of dollars in investments. It all depends on what “machine” you want to run.
The terms of launching the basic functionality, taking into account the fact that there are no ready-made solutions on the market and even 1C covers only 50% of the development, start from 6 months, and at the same time, the marketplace platform will require constant refinement and development.
Payback also has a floating number. In our experience of working with different strategies, we have not seen a period less than 5 years. But here, too, everything depends on many factors.
Ultimately, you should have a serious IT platform with a large number of information systems, each of which will be responsible for individual components of the marketplace.
Again, don’t try to implement everything in one ERP system, which by default can only cover order management (OMS) and nothing else. Each component in a microservice architecture must be functionally isolated, integrated with others, and developed locally.
It is this approach that will make it easy to develop your platform, without running into technological and architectural constraints, and to increase the volume of your business.




