Edge computing and 5G – the future of use. Dell Technologies view
Dell Technologies is expanding its portfolio of edge solutions with new offerings. They help overcome the fear of Edge Computing, allow you to fully appreciate the benefits of new technologies and minimize concerns about pitfalls during their implementation. The innovations are designed to help customers solve the problems of unlimited data at the boundaries of IT infrastructure.
More recently, the topic of “big data” has been extremely popular among manufacturers and users of IT solutions. Collecting, storing and analyzing huge amounts of data was a truly challenging task. But that was back when the data was “just” big. The challenge back then was to provide the data center with enough memory and processing power to store and process all of this big data.
Fast forward a few years, and the task will go beyond the walls of the data center. The well-known analytical agency Gartner predicts that by 2022, as a result of the introduction of innovative technologies, 75% of data generated by enterprises will be created and processed outside the traditional data center or cloud, while today no more than 10% of such data is created in modern enterprises. But this data is not traditional data, its volume is almost unlimited, and it is time dependent, having a limited lifespan. Their source is mobile phones and consumer devices. Capitalizing on this class of data requires obtaining and processing information almost at the time of creation – quickly, economically and securely.
New era of data poses new challenges for IT
It is easy for end users to think of data as intangible bits of information that magically appear at their fingertips when they are needed. For IT employees, big data is primarily associated with the large capacity and cumbersome means needed to process it. And when you combine big data with decentralized data creation and consumption, a whole host of new IT challenges emerge.
Innovative organizations that are trying to implement new technologies as they emerge are rethinking the placement of applications and infrastructure, moving them as close to the data creation point as possible. Moving the IT infrastructure outside the data center creates a number of constraints that need to be removed to improve the success of projects:
- Remote Location: Leads to limited bandwidth and network connections.
- Environment: located in “field conditions” where external influences such as dust, temperature changes, etc. are not excluded.
- Dimensions: the need to be prepared for placement in confined spaces.
- Electricity: Power and cooling conditions are very different from those of a data center.
- Control and management: located away from qualified IT personnel.
- Security and protection against unauthorized access: IT departments must control security outside the data center.

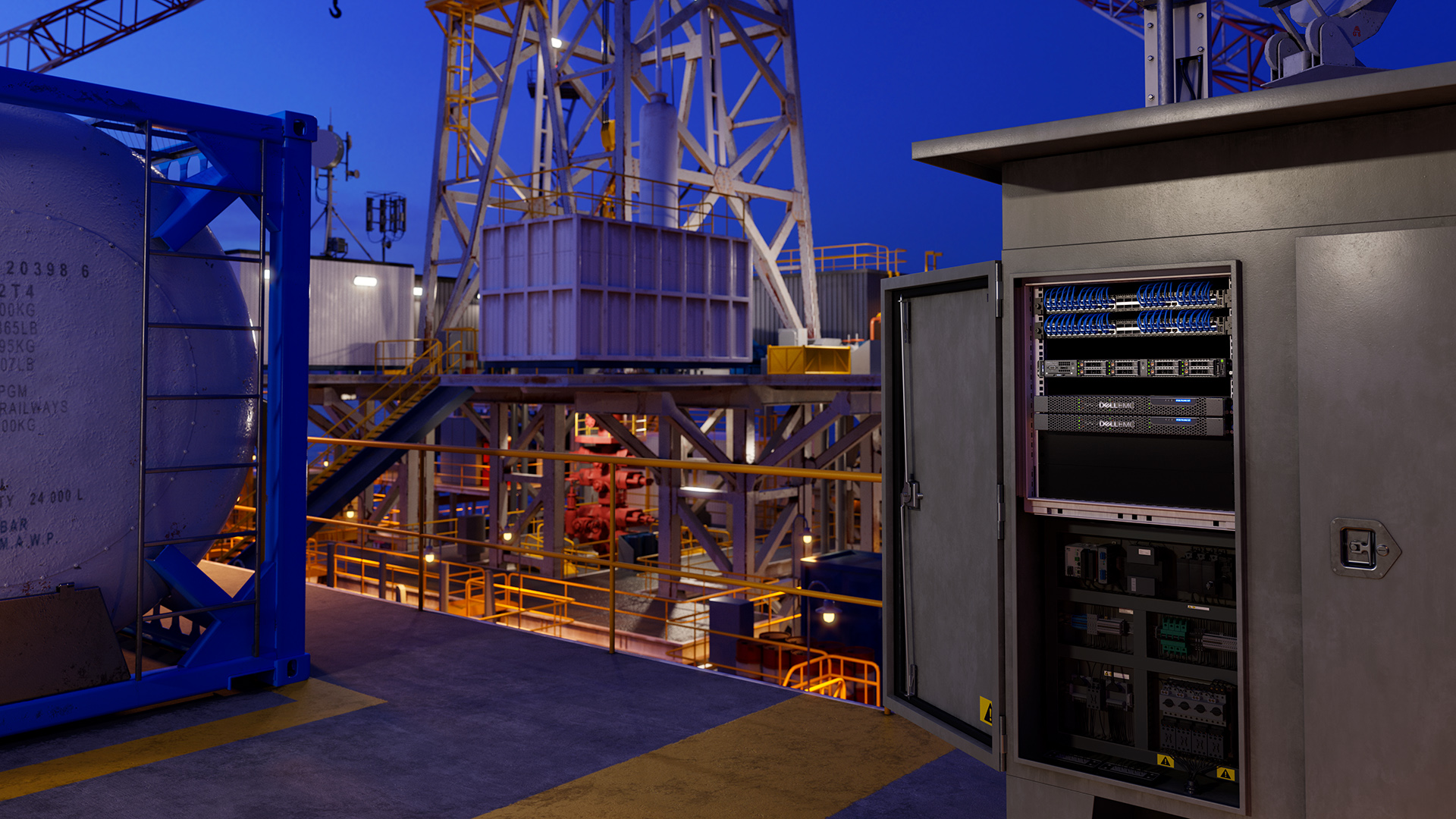
Consider the topic of edge computing through the prism of implementing new business models using 5G technologies based on data – processing data from “things” and devices in real time, when decisions must be made quickly: before the data becomes irrelevant. That said, it’s important to consider how 5G is driving edge development by providing a disaggregated cloud user plane that allows apps and services to connect closer to things and devices (and with less latency). 5G and edge computing are symbiotes of sorts, although both have use cases that are independent of each other.
There is still a lot of uncertainty about what a typical edge computing hardware installation would look like, but one thing is certain: there are no two identical edge computing deployments. Many questions need to be answered when designing a solution, including:
- What use cases will justify the investment: support of operations (due to the presence of an extensive network of branches or divisions of the organization) or the main business objectives (due to the key requirements of the business strategy)?
- What are the unique requirements of the industry?
- How significant will the operating savings be?
Each situation is different. The edge infrastructure needs to be very flexible to support multiple use cases. A homogeneous public cloud infrastructure deployment model built using shared building blocks that scale within a rack, then within a row in a data center, and then within a data center, is giving way to a heterogeneous infrastructure model at the IT infrastructure edge. The key to success is having a flexible set of hardware solution capabilities that can be used to support specific requirements when working at the edge of the IT infrastructure, including:
- Ability to use multiple computing accelerators on a common platform. This requires an infrastructure with x86 servers and storage class memory (SCM) using GPU, FPGA, or SmartNIC acceleration technologies. This will enable the infrastructure to meet complex requirements to support video streaming, edge transcoding, or any other feature that requires acceleration at the IT edge.
- A flexible form factor infrastructure suitable for different environments, use cases, and performance requirements. Infrastructure deployed outside of a controlled environment needs to be strengthened to cope with harsh conditions. It should be of a dense form factor and shallow depth for installation in confined spaces. The telecommunications network is still defined as a front-access network with minimum rack depth, DC powered, NEBS certified.
- The key is to align with the architecture of the 5G Cloud Native and Virtualized Network features. It helps to simplify overall network architecture, reduce deployment costs and improve customer experience by centralizing 5G radios while distributing vEPC functionality.
- The ability to provide access for remote control, as well as automation of routine administration processes. Speaking about the manageability of hardware solutions at the IT edge, it would be useful to be able to provide a set of APIs that allow integrating the management automation system for these solutions into external orchestration systems.

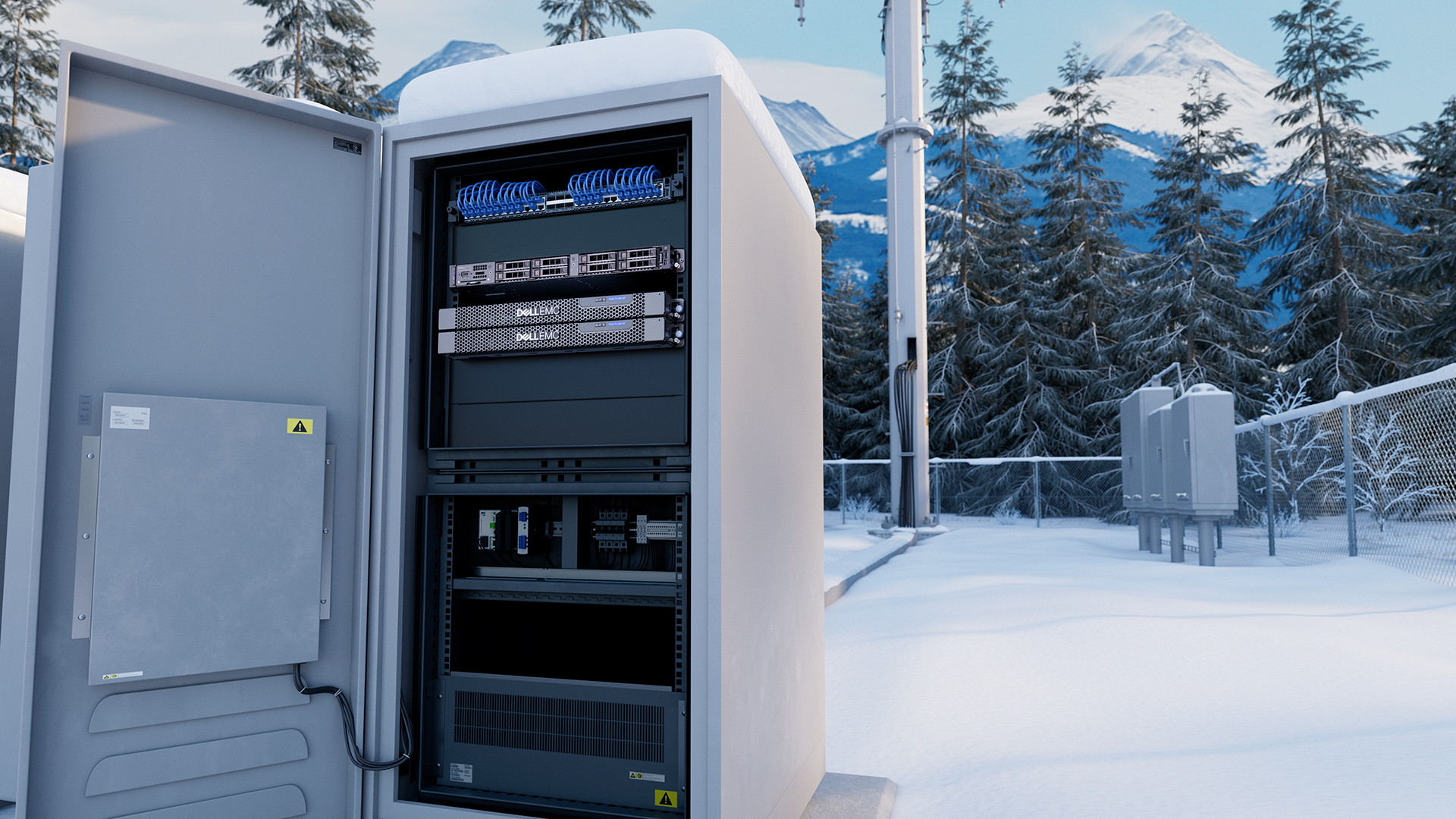
Overcoming Boundary Constraints with New Dell Technologies Solutions
New server Dell EMC PowerEdge XE2420 Supports edge computing and analytics in tight spaces, it is capable of operating outside the data center in harsh environments. It is a reliable server that provides maximum performance for complex edge applications while meeting the ever-increasing demands for computing resources, low latency and high bandwidth network interfaces.
- 2-socket full-featured server in a compact design, 444 mm (17.4 ”) deep.
- Supports the installation of up to 4 computing accelerators and up to 92 TB of internal disk space, combining computing density and large capacity in a compact form factor.
- A wide range of storage options including solid state drives and NVMe.
- Provides extensive remote control, streaming telemetry and automation capabilities using the iDRAC remote access controller including Redfish support.
- Designed for harsh environments outside the data center over an extended temperature range of 5 ° C to 40 ° C (41 ° F to 104 ° F).
Detailed description of the server here…

Dell EMC PowerEdge XR2 Extremely Secure Server
Dell Technologies Specialized Edge Computing Model 2 – Server PowerEdge XR2specially designed for extreme working conditions. It surpasses shock, vibration, dust, humidity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) certifications for military and marine applications.
Dell EMC PowerEdge XR2 Features:
- Up to two 24-core Intel Xeon processors (up to 150W each).
- Up to 2 TB of RAM.
- Up to 8 onboard storage including NVMe SSD support.
- 2 x PCIe slots.
- 2 built-in 1 Gbit ports, optional support for 25 Gbit Ethernet.
- Up to 2 hot-swappable 550W power supplies.

New remote control controller IDRAC9: maximum control from data center to infrastructure border
The ability to remotely manage infrastructure at the IT border is provided by a new remote access controller built into all systems iDRAC9… With the activation of an additional license (datacenter license), it acquires the ability to collect streaming telemetry. IT professionals can now use artificial intelligence technologies to obtain information about the management of all systems, regardless of whether they are installed in the data center or on border IT infrastructure. Because streaming provides 10,000 times more remote management efficiency than traditional server health, the reliability and control of the infrastructure at the IT edge is greatly enhanced by administrators.
While fear is a natural feeling that transcends your data center, the Dell Technologies team is always ready to help you replace it with the pleasure of using cutting edge technology in your work. We partner with customers at every stage of the interaction, bringing people, processes and technology together to accelerate innovation and help you bring it to your organization. If you have a specific request for the implementation of a complex project, then we are always happy to help you in private messages.
Author: Igor Korolevsky, Consulting Engineer, Computing and Networking Department, Dell Technologies