Continuous security testing and automated cyber risk assessment with the Cymulate platform
The purpose of continuous security testing, also called “security performance testing”, using the Cymulate platform is to determine how effective the organization’s current security measures are, to identify new security vulnerabilities as they arise, and to significantly reduce and continually optimize. an organization’s attack surface. Using automatic alerting and reporting, security teams can immediately get a proactive vulnerability assessment to take action to remediate them.
Continuous security testing is performed using automated technologies such as hack and attack simulations, according to a recent SANS Institute survey. Currently, 28% of security professionals use BAS to test their security controls.
Benefits of Continuous Security Testing
Reiterating the general shift from binary security solutions at a specific point in time to a more continuous and adaptive approach to implementing an information security strategy, there is a continuous cyber risk assessment taking into account the reality of IT environments that are in constant motion, along with threats, and require more. focus and resources for early detection and response, not just predominantly protection (see the CARTA Gartner model).
By implementing Cymulate (BAS) continuous security performance testing, organizations can better meet the following challenges:
The daily emergence of new types of attacks – new variants of ransomware, Trojans, cryptominers and crypto stealers that appear every day and require preventive control updates taking into account the latest compromising data (IoC). Manually verifying that the ISS can block the latest phishing sites, infection points, C2 servers, etc. is time consuming and impractical for large organizations with distributed security controls. IoC’s constant modeling of the latest threats means that security teams can counter them faster.
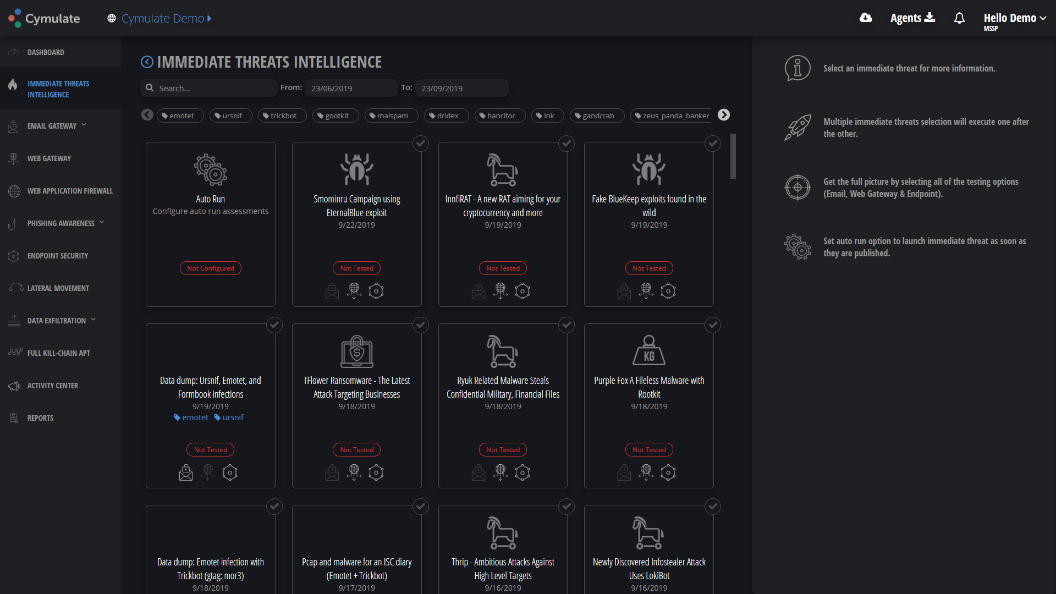
Figure 1. Continuous security testing helps you meet the latest threats faster.
Evolving stealth techniques – IoC-based proactive controls are useless against unsigned and fileless attacks, making behavior-based detection tools such as tricksters, EDRs, and EUBA tools essential to detect them. But how do you know if your machine and AI solutions are effective against these threats? By continually testing their effectiveness against simulated cyberattacks, organizations can continually tweak the configuration settings of these tools to ensure they are detected more quickly.
Frequent changes in the IT environment. Every day, IT environments change, be it deliberate changes in network policy, the use of hidden IT infrastructure, new employees or leaving the company, the introduction of new software, hardware or virtual environments. Proactively assessing the impact that these changes can have on an organization’s security posture eliminates blind spots that can potentially become unpleasant surprises.
Limited work resources and budget. Continuous testing of security effectiveness helps you make the most of your limited resources and budget. By continually identifying gaps and prioritizing recovery according to where vulnerabilities are greatest, security teams can improve security with less resources. In addition, with the tools and know-how to improve their security, organizations can begin to reduce their reliance on manual tests by limiting them to pinpoint detections or regulatory compliance.
State subjects of threats. Dozens of APT groups have been found to work for governments for financial, political and military gains. These groups have the money, time, and skills needed to carry out complex, continuous attacks. By continually improving security controls against the techniques these groups have already used, organizations can better and more timely detect these threats.
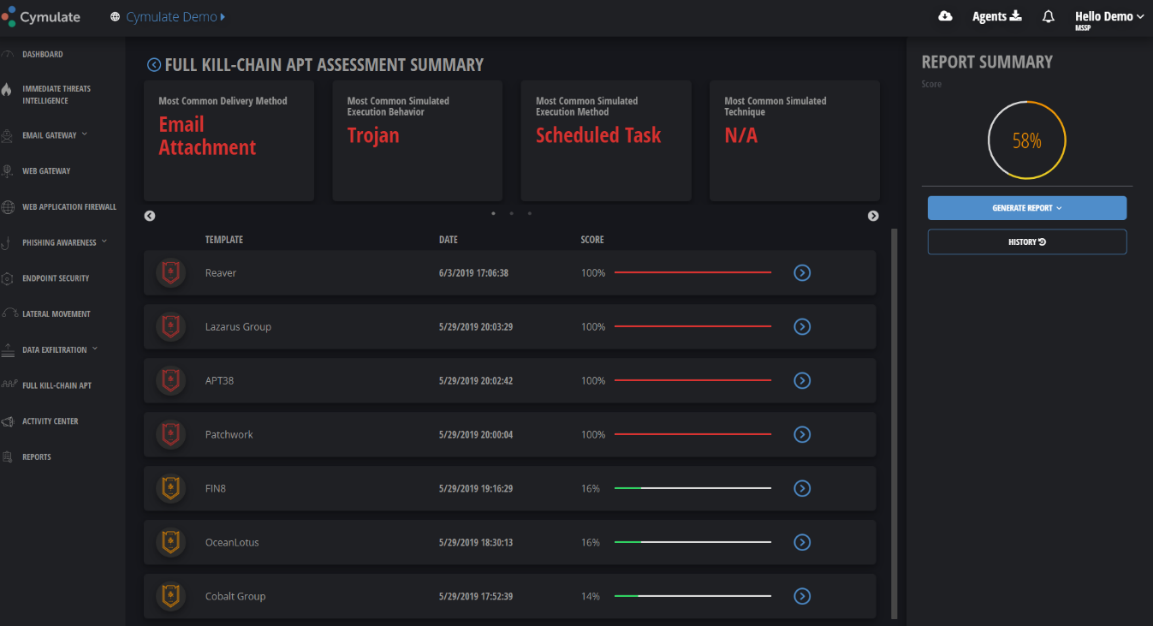
Figure 2: Continuous testing allows customization of controls for APT government groups
External contact points and attacks on supply chains. Consumer-centric portals, health information exchange (HIE), financial services through payment gateways and ACH, and enterprises using common collaboration tools are all security threats to an organization. Configuration testing, including testing controls such as WAF (to prevent CapitalOne style hacking), email gateways, infrastructure controls that restrict lateral displacement, and others, is critical to mitigating cyber risk posed by these touchpoints, and preventing attacks on supply chains.
How it works
So how do you get the cyber risk score? Using automated simulations of the Cymulate hack and attack, the security teams:
- Simulate cyber attacks at all stages of hacking (kill chain).
- Evaluate controls based on identified vulnerabilities.
- Correct impacts using actionable assessment.
- Repeat hourly, weekly, daily, or any specified frequency.

Figure 3: Continuous security testing in 4 steps
Continuous testing against persistent threats
The latest versions of ransomware, compromised business email, and government APT campaigns call for a change in cybersecurity strategy. With the Cymulate platform, by continually improving security controls, identifying security vulnerabilities, and tuning them for efficiency gains, security teams can continually reduce their attacks and improve the overall security posture of an organization.
Article prepared Softprom – official distributor Cymulate, from which you can order a free consultation on products.
And on our platform you can learn more about Cymulate BAS, implementation results and competitive products.