Automated control system for a mining excavator

Introduction
The excavator can be seen at any construction site in the city. An ordinary excavator is handled by one driver. To manage it does not require a complex automation system.
But if the excavator is many times more familiar and reaches the height of a five-story building, can a Land Cruiser be placed in its bucket, and the “filling” consists of electric motors, cables and gears the size of a car? And does he work in coal and mining quarries, 24 hours a day / 7 days a week 30-40 years in a row?
Such an excavator is an industrial system, the maintenance of which is very expensive.
Automation of technological processes reduces the cost of operating an industrial system. An automated process control system is called – ACS TP. An excavator similar to the one described is no exception.
So what kind of excavator is this? What process control system is used on it?
What kind of excavators are we talking about?
We are talking about mining excavators. These machines develop mining and coal quarries.
Dimensions: mining excavators reach the height of a five-story building.
Moving: The excavator moves with the help of a tracked undercarriage. The cart consists of:
- tracked frames;
- caterpillars
- travel drives;
- lubrication circuit of the undercarriage.
Digging: For digging, mining excavators use the “Direct Shovel” mechanism. The mechanism consists of a bucket, stick and boom. The bucket is mounted on the handle. The handle is designed to give the bucket translational movement. It is located transverse to the boom. A pressure mechanism is installed on the boom, which carries out pressure and return movement of the handle with a bucket. A complex system of ropes sets this mechanism in motion.
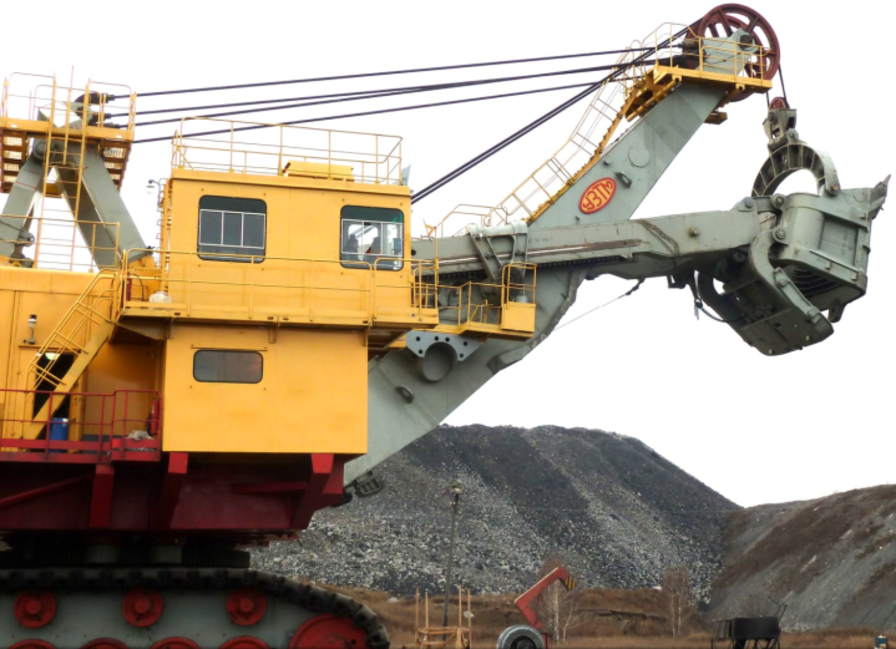

Device (composition): The excavator consists of three enlarged units:
- working equipment;
- rotary platform with mechanisms;
- running trolley.
The working equipment has been described above – this is precisely the mechanism of the “Direct shovel”.
Mining excavators perform many operations: digging, turning the body of the machine, moving, etc. A separate engine is designed for each operation. To perform all these operations requires a huge number of systems. All systems and mechanisms, as expected, are located in the "computer room".
The machine room of an excavator is a turntable. It contains a bucket lifting mechanism, a rotary mechanism, an electric equipment of an excavator with a control and monitoring system, auxiliary mechanisms, a pneumatic system, a centralized automatic lubrication system.
Working conditions and service life: mining excavators work 24/7, and the service life is really 30-40 years.
Food / Fuel: walking excavators are powered by electricity. Each mountain section of the section receives electricity from a substation with a voltage of 35/6 kV.
What is the automation of excavators on board?
A wheeled excavator is an industrial system. The tasks of operating an excavator are similar to those of operating an industrial facility:
- control of the parameters of the movement system;
- equipment wear monitoring;
- protection of equipment from external and internal threats: overload, short circuits, etc .;
- energy metering;
- excavator position control;
- inspection of equipment during operation;
- blind spots control;
- excavator performance monitoring;
- event logging;
- data transfer for centralized accounting.
All these tasks are handled by one operator. This is possible through automation.
Automated control system “on board” of the excavator includes the following systems:
To monitor movement parameters controllers are installed. The operator monitors the following parameters: operation of drive control systems, heating temperature of system components, pressure in the pneumatic system, and grease.
To account for consumed and given active and reactive electric energy an electricity meter is installed.
Blind areas, mechanical equipment and working face are displayed on the operator screen. For this, video cameras are installed.
For calculation and accounting excavator performance data from controllers are used. The indicators are calculated for a certain time interval: per shift, per month, by teams.
All events are saved in the event log and the required time interval is stored.
How is data transfer organized?
As mentioned above, the excavator consists of a running trolley and a turntable.
The turntable can rotate freely 360 degrees relative to the undercarriage. It is very problematic to use wires to transfer data between these two parts. They grind very quickly.
Data between parts of the excavator is transmitted over Wi-Fi. Phoenix Contact's Wi-Fi WLAN 5100 function modules are installed in the base and turntable together with special RAD-CAB-EF393-10M cables and RAD-ISM-2459-ANT-FOOD-6-0-N omnidirectional antennas. In total, 3 antennas are installed on the excavator for stable communication.
The excavator also has a 4G TC ROUTER 3002T-4G router with a TC ANT MOBILE WALL 5M wide-directional antenna and CSMA-LAMBDA / 4-2.0-BS-SET surge protection device.
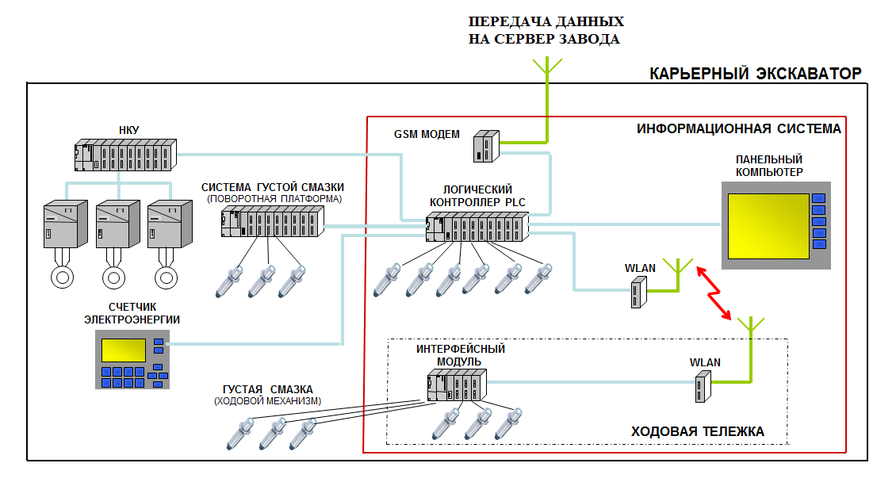
Block diagram of a mining excavator information system
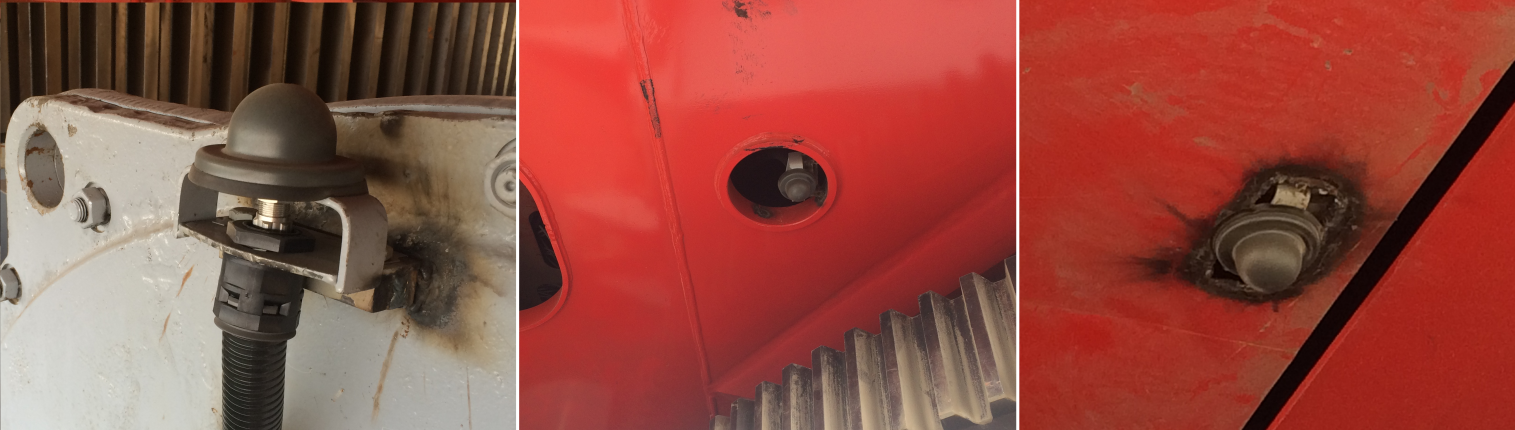

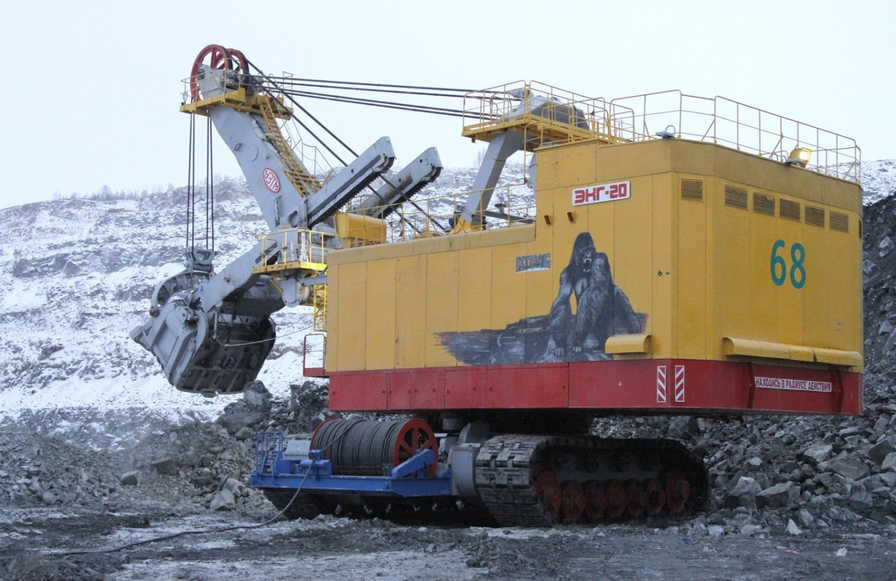
Installation of antennas on an ECG-20 excavator
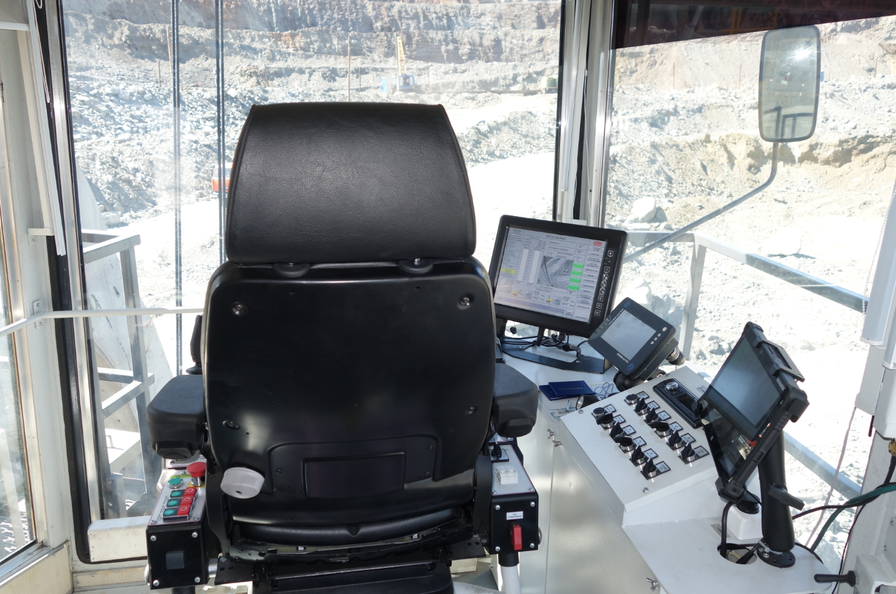
What does the operator's cab look like?
The final automation result for the operator is as follows: