5. FortiAnalyzer Getting Started v6.4. Maintenance and licensing

Hello! Welcome to the final lesson of the course FortiAnalyzer Getting Started… This lesson will be purely theoretical: in it we will consider all the points that are related to the maintenance of the device and for some reason were not included in the previous lessons. We will also look at the licensing scheme FortiAnalyzer… The material of this lesson is presented under the cut in the form of an article, as well as in the form of a video tutorial.
Depending on the infrastructure, it may be necessary to distribute administrative tasks among different users. In this case, multiple administrative accounts can be created on FortiAnalyzer. But it should be understood that each new administrator increases the risk of a network security breach.
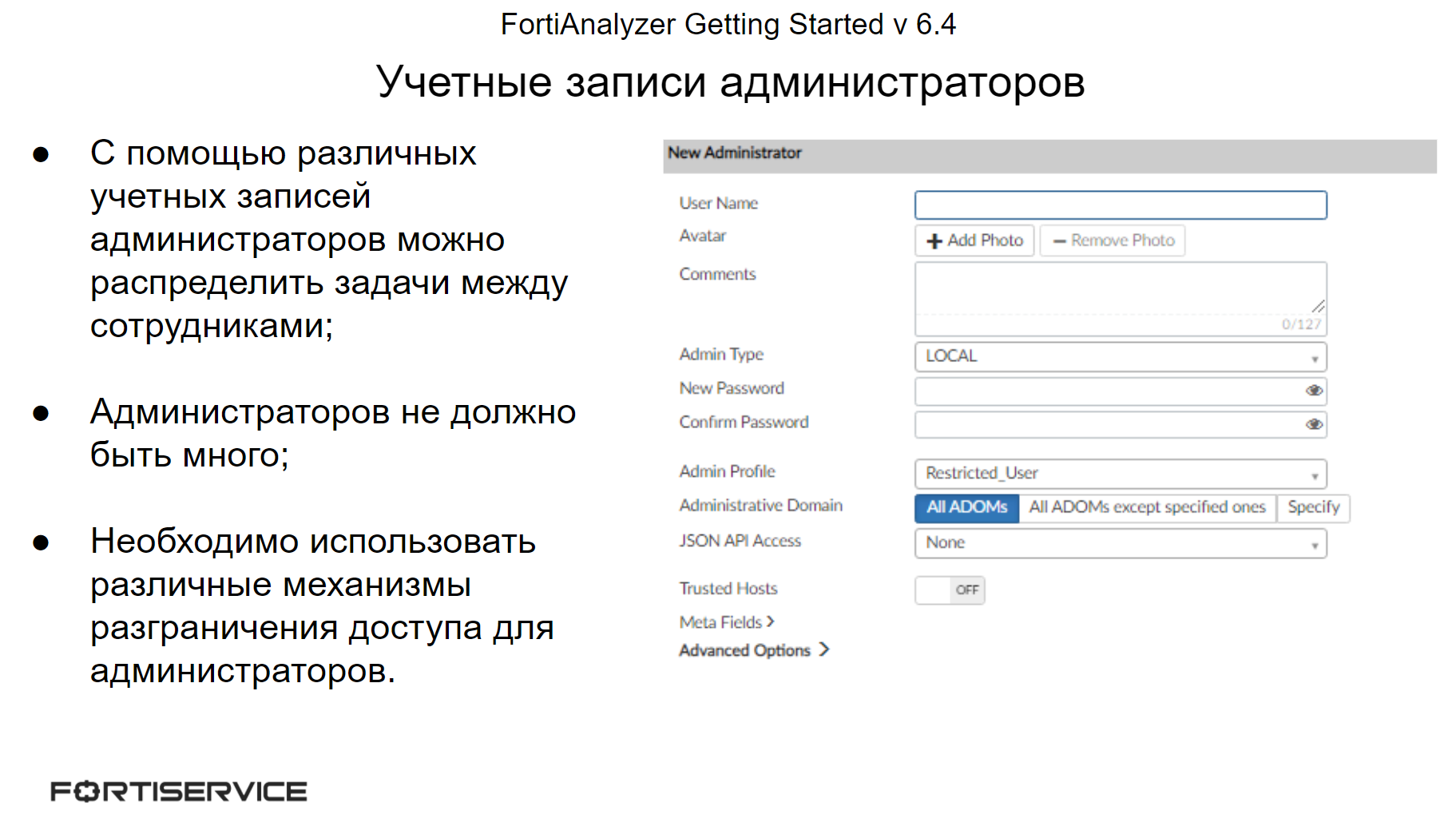
To increase the level of network security, you can use several methods to control administrative access:
Administrator profiles;
Trusted hosts;
Administrative domains.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these methods.
When creating different administrator accounts, you should not give them more privileges than are necessary to complete their tasks. FortiAnalyzer uses an administrator profile mechanism for this purpose. Each profile contains a list of privileges available to the administrator. The system has three pre-configured administrator profiles:
SuperUser – provides access to all system and device management privileges;
StandartUser – provides access to device management privileges, without system privileges;
Restricted_User – provides access to read device settings, without system privileges.

You can also create your own administrator profiles with your own set of privileges. Each administrator account must have one of the existing profiles applied.
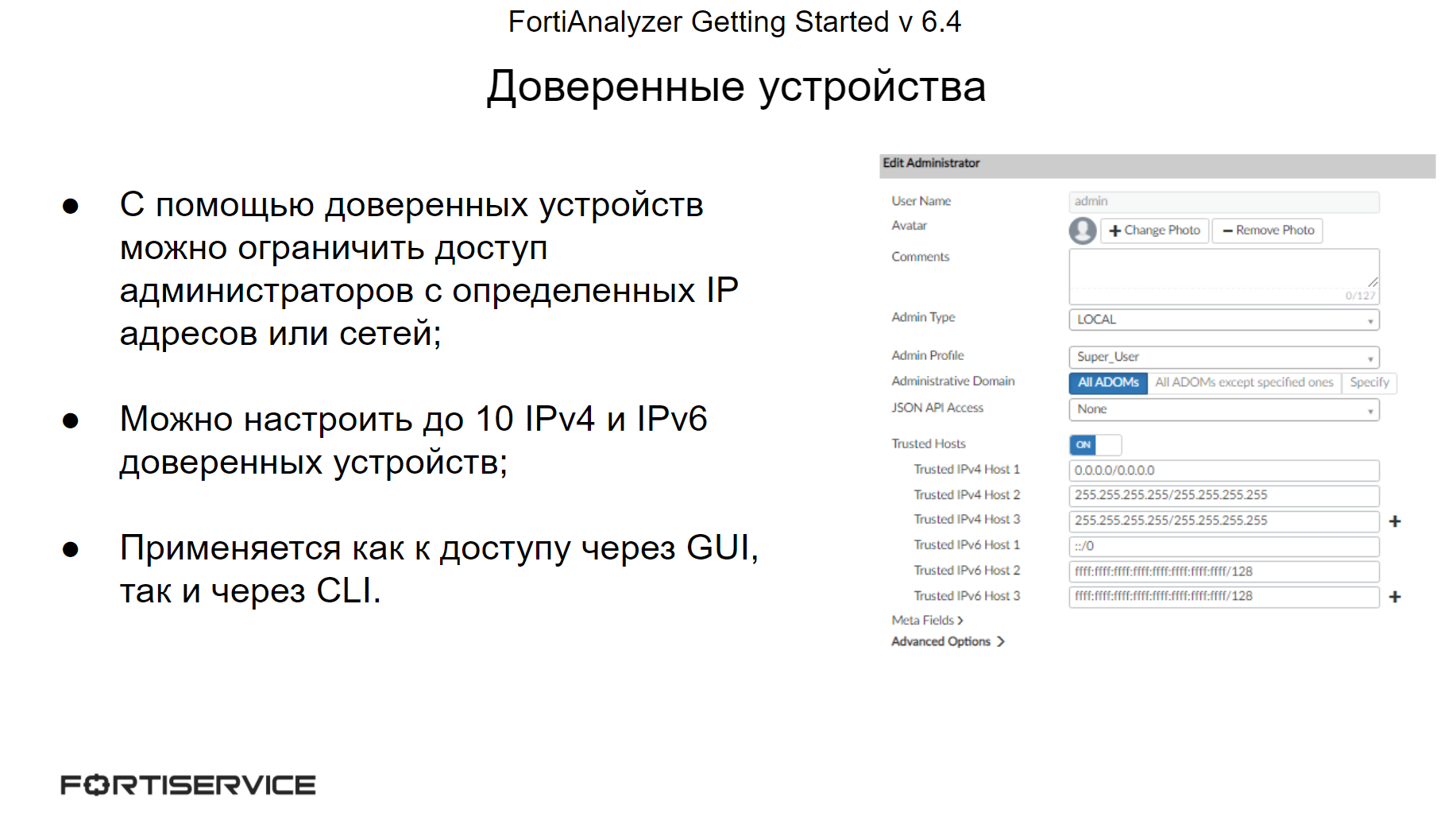
In addition to administrator profiles for access control, you can configure trusted devices for each administrator account. They allow you to provide administrator access only from specific IP addresses – devices or subnets. For example, if you configure one trusted device with an IP address of 192.168.232.10, then this administrator will be able to connect to FortiAnalyzer only from this IP address, from others, access will be denied.
Moreover, control through trusted devices applies to both the Web interface and the CLI interface when accessing via SSH.
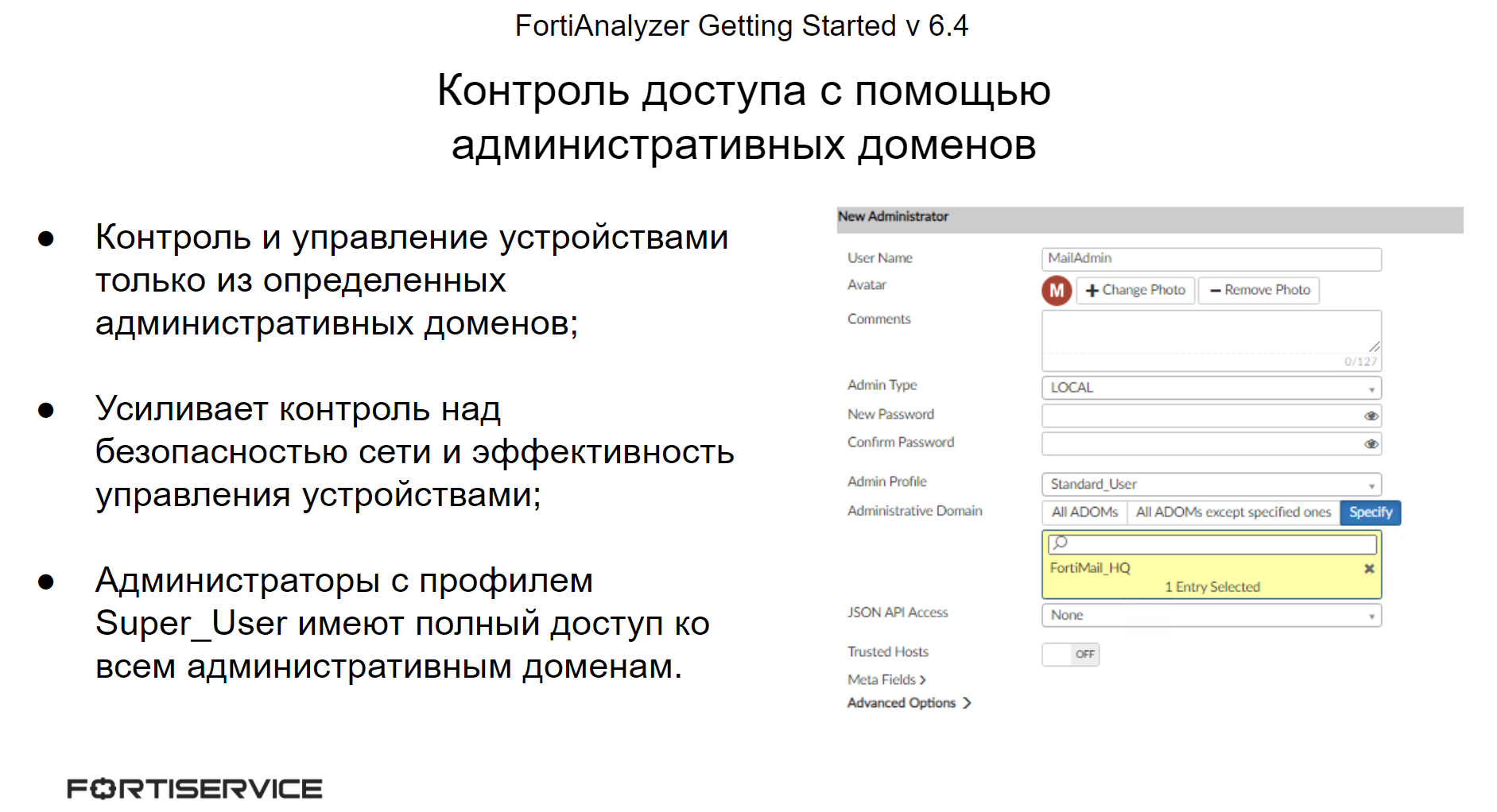
Another access control mechanism is administrative domains. Using administrative domains enhances device management efficiency because each administrator only needs to manage devices that belong to specific administrative domains. It also increases the level of security, since each administrator is limited to control only those devices to which he should have access.
An administrator with the Super_User profile has full access to all administrative domains. Administrators with different profiles have access only to those administrative domains to which they are linked – this can be one or more domains.
Instead of creating administrators locally, you can bind external authentication servers to FortiAnalyzer. LDAP, RADIUS, TACATS +, and PKI can be used to verify external administrators. When using multiple authentication servers, each server must be bound separately.

Using various monitoring mechanisms, you can track the behavior of administrators, as well as the execution of ongoing actions. In field System Settings> Admin> Administrators you can see the sessions of administrators: who is currently active, as well as their trusted devices. By default, only administrators with the Super_User profile have access to this list.
You can track the activity of administrators using the menu System Settings> Event Log… Various administrator actions are listed here, such as configuration changes, and successful or unsuccessful login attempts.
On the menu System Settings> Task Monitor you can track the status and progress of tasks running on FortiAnalyzer.

Registered devices can be moved between administrative domains. However, you should not do this until it is strictly necessary. As one example, one administrative domain contains several devices, and some of them generate too many logs, while others, on the contrary, generate few logs. In such a situation, it is recommended to place devices with a high level of log generation in one administrative domain, and devices with a low level in another. This approach helps to efficiently manage the available space in each administrative domain.
In addition to creating a new administrative domain for the move, you can edit an existing administrative domain and add the device you want to move there during the editing process.
Note that when updating the FortiGate operating system, there is no need to move it to a new administrative domain.

Before moving a device to a different administrative domain, there are a few things to consider, especially if the device being moved has already collected logs from the old administrative domain:
It is necessary to check if the allocated disk space is sufficient for the needs of the device being moved;
Do you need existing analytics logs in the new administrative domain? If so, after moving the device, you need to rebuild the database in the new administrative domain.
Do I need existing analytics logs in the old administrative domain? If not, after moving the device, you must rebuild the database in the old administrative domain. Otherwise, these logs will be deleted in accordance with the data retention policy in the old administrative domain.

The rest of the points related to the maintenance of the device were discussed in one form or another in the previous lessons. Therefore, let’s move on to licensing FortiAnalyzer. For convenience, items that make up the annual cost of ownership are highlighted in green. There are 5 options for purchasing a device:

The first option is a physical device and a subscription package that also contains technical support – in one SKU. Convenient for initial purchase. The annual cost of ownership is already a separate subscription package that includes technical support. You can also buy the RMA service separately, in which case its price will also be included in the cost of annual ownership. Note that the SOC service is not available for the FortiAnalyzer 200F hardware device.
The second option is a separate SKU for a physical device, as well as a separate SKU for a subscription package that includes technical support. Usually it is more expensive than the first option. The annual cost of ownership is also a subscription package that includes technical support. You can also buy the RMA service separately, in which case its price will also be included in the cost of annual ownership.
The third option is a separate SKU for a physical device, as well as separate SKUs for each type of subscription (IOC or SOC), as well as separate SKUs for technical support and RMA. In this case, the selected individual SKUs for services, technical support and RMA will constitute the annual cost of ownership, unless their composition changes upon renewal.
The fourth option is a separate article for the basic virtual machine, as well as an optional separate article for expanding memory, it is also a one-time, then articles for technical support and IOC and RMA services. The annual cost of ownership in this case is the technical support service and the selected IOC and RMA services.
And the last option – separate SKUs for the basic virtual machine and memory expansion, a separate SKU with a subscription package that includes technical support and IOC and SOC services. Also optional item is RMA service. The annual cost of ownership in this case is considered as the subscription price, and the RMA price if it is also selected for purchase.
Note that the annual cost of ownership can change: there is an opportunity to buy other services, or vice versa, when renewing, buy fewer services than before.
Below is a video in which all the above information is presented in video format:
This is where we want to end this course. As noted at the beginning, the course turned out to be not too voluminous, we tried to briefly describe the basic principles and capabilities of the FortiAnalyzer product. We hope that this course will be useful for those who are just getting acquainted with Fortinet products, and with FortiAnalyzer in particular. Periodically, we publish articles, videos, and courses on various Fortinet products. In order not to miss them, stay tuned to our resources:





